- What are you mining in bitcoin
- How does Bitcoin mining work?
- Isn’t Bitcoin mining a waste of energy?
- How does mining help secure Bitcoin?
- What do I need to start mining?
- What does MH/s, GH/s mean?
- What does W/Gh and W/Th mean?
- How do I calculate my Bitcoin mining profitability?
- What does hashing mean?
- What is a Bitcoin mining pool?
- What does GPU stand for?
- What is a Bitcoin mining share?
- What is a Bitcoin mining module?
- What does ASIC stand for?
- What does FPGA stand for?
- Where can I view mining data about each block?
- What are you mining in bitcoin
- What is Bitcoin Mining?
- What is the Blockchain?
- What is Proof of Work?
- What is Bitcoin Mining Difficulty?
- The Computationally-Difficult Problem
- The Bitcoin Network Difficulty Metric
- The Block Reward
- Bitcoin Mining Guide — Getting started with Bitcoin mining
- How Bitcoin Mining Works
- Step 1 — Get The Best Bitcoin Mining Hardware
- How To Start Bitcoin Mining
- Best Bitcoin Cloud Mining Services
- Bitcoin Mining Hardware Comparison
What are you mining in bitcoin
Mining is the process of spending computing power to process transactions, secure the network, and keeps everyone in the system synchronized together. It can be perceived like the Bitcoin data center except that it has been designed to be fully decentralized with miners operating in all countries and no individual having control over the network.
This process is referred to as «mining» as an analogy to gold mining because it is also a temporary mechanism used to issue new bitcoins. Unlike gold mining, however, Bitcoin mining provides a reward in exchange for useful services required to operate a secure payment network. Mining will still be required after the last bitcoin is issued.
How does Bitcoin mining work?
Anybody can become a Bitcoin miner by running Bitcoin mining software and Bitcoin mining modules with specialized Bitcoin mining hardware. Mining software listens for transaction broadcasts through the peer-to-peer network and performs appropriate tasks to process and confirm these transactions. Bitcoin miners perform this work because they can earn transaction fees paid by users for faster transaction processing, and newly created bitcoins issued into existence according to a fixed formula.
For new transactions to be confirmed, they need to be included in a block along with a mathematical proof of work. Such proofs are very hard to generate because there is no way to create them other than by trying billions of calculations per second. This requires miners to perform these calculations before their blocks are accepted by the network and before they are rewarded. As more people start to mine, the difficulty of finding valid blocks is automatically increased by the network to ensure that the average time to find a block remains equal to 10 minutes. As a result, mining is a very competitive business where no individual miner can control what is included in the block chain.
The video below of a Bitcoin mining farm in China will give you a better idea of just how competitive Bitcoin mining has become:
The proof of work is also designed to depend on the previous block to force a chronological order in the block chain. This makes it exponentially difficult to reverse previous transactions because this requires the recalculation of the proofs of work of all the subsequent blocks. When two blocks are found at the same time, miners work on the first block they receive and switch to the longest chain of blocks as soon as the next block is found. This allows mining to secure and maintain a global consensus based on processing power.
Bitcoin miners are neither able to cheat by increasing their own reward nor process fraudulent transactions that could corrupt the Bitcoin network because all Bitcoin nodes would reject any block that contains invalid data as per the rules of the Bitcoin protocol. Consequently, the network remains secure even if not all Bitcoin miners can be trusted.
Isn’t Bitcoin mining a waste of energy?
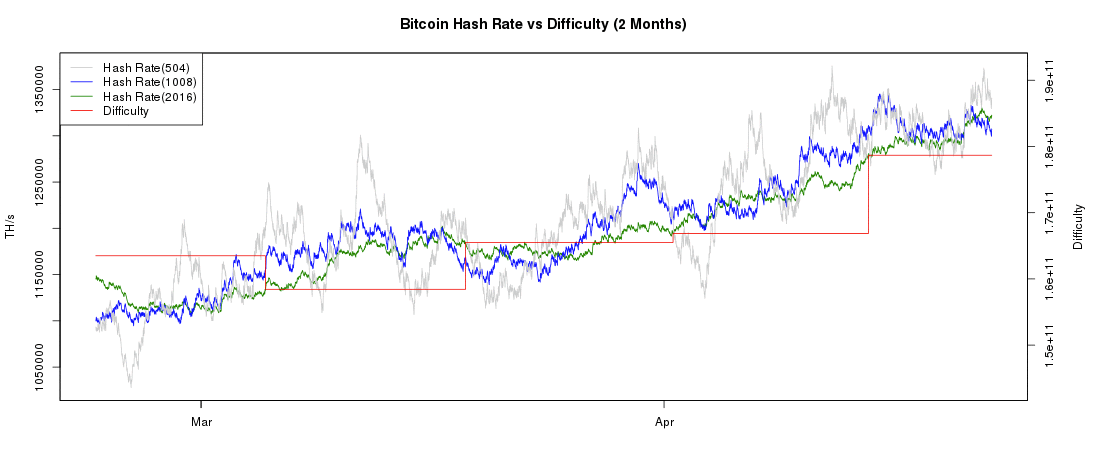
Spending energy to secure and operate a payment system is hardly a waste. Like any other payment service, the use of Bitcoin entails processing costs. Services necessary for the operation of currently widespread monetary systems, such as banks, credit cards, and armored vehicles, also use a lot of energy. Although unlike Bitcoin, their total energy consumption is not transparent and cannot be as easily measured. The total Bitcoin network hash rate is publicly available and can be used to estimate the network’s total electricity costs.
Bitcoin mining has been designed to become more optimized over time with specialized hardware consuming less energy, and the operating costs of mining should continue to be proportional to demand. When Bitcoin mining becomes too competitive and less profitable, some miners choose to stop their activities. Furthermore, all energy expended mining is eventually transformed into heat, and the most profitable miners will be those who have put this heat to good use. Some miners, for example, [use the heat generated by bitcoin miners to supplement regular heating systems](http://www.waters.nyc/writing/325).
An optimally efficient mining network is one that isn’t actually consuming any extra energy. While this is an ideal, the economics of mining are such that miners individually strive toward it.
How does mining help secure Bitcoin?
Mining creates the equivalent of a competitive lottery that makes it very difficult for anyone to consecutively add new blocks of transactions into the block chain. This protects the neutrality of the network by preventing any individual from gaining the power to block certain transactions. This also prevents any individual from replacing parts of the block chain to roll back their own spends, which could be used to defraud other users. Mining makes it exponentially more difficult to reverse a past transaction by requiring the rewriting of all blocks that occurred after the target transaction.
What do I need to start mining?
In the early days of Bitcoin, anyone could find a new block using their computer’s CPU. As more and more people started mining, the difficulty of finding new blocks increased greatly to the point where the only cost-effective method of mining today is using specialized hardware.
What does MH/s, GH/s mean?
These abbreviations stand for the hashing power that your miner is generating. MH/s stands for megahash per second and GH/s stands for gigahash per second. There is a direct correlation between how fast your miner works and how profitable it will be.
What does W/Gh and W/Th mean?
W/Gh and W/Th are abbreviations for watts per gigahash and watts per terahash. These metrics calculate how many hashes a miner can run per watt of electricity. Mining hardware with lower W/Gh and W/Th are more efficient. Currently, the Antminer S7 and Avalon6 are the most efficient miners available for purchase, at 0.25 W/Gh and 0.29 W/Gh, respectively.
How do I calculate my Bitcoin mining profitability?
You can use bitcoin mining profitability calculators to calculate the profitability of mining under a variety of circumstances, to include difficulty increases, power consumption, and average hashrate, for example.
What does hashing mean?
The term «hashing» means how quickly your hardware is processing data from the Blockchain and solving the complex mathematical equations that are required to earn bitcoins.
What is a Bitcoin mining pool?
A mining pool is a group of miners who have shared their hashing resources to solve blocks together and the rewards are then distributed amongst the members.
Let’s say Bob runs a Bitcoin mining farm with 1% of the Bitcoin network hash rate. His machines only find, on average, one out of every 100 blocks. Bob becomes impatient and wants more frequent payouts. He joins a mining pool with 20% of the network hash rate. Instead of getting paid on average once per 100 blocks, Bob now receives smaller but more frequent payouts every five blocks.
What does GPU stand for?
A Graphics Processing Unit powers most computer video cards and can be used to mine Bitcoins.
What is a Bitcoin mining share?
A share is merely an accounting method to keep the miners honest and fairly divide any rewards earned by the pool.
What is a Bitcoin mining module?
A Bitcoin mining module is usually a worker as assigned in the Bitcoin mining software. For example, four GPUs are plugged into the motherboard constituting the Bitcoin mining hardware. Then the Bitcoin mining software identifies each GPU as a unique worker. So, this small Bitcoin mining rig would be composed for four Bitcoin mining modules.
What does ASIC stand for?
An Application-Specific Integrated Circuit is a special chip designed specifically for mining Bitcoin and is much more energy-efficient and faster than GPU or FPGA mining.
What does FPGA stand for?
A Field-Progammable Gate Array was already an established hardware product that can be used for different purposes, but in this case the technology was repurposed for mining Bitcoin.
Where can I view mining data about each block?
The mining rewards and transaction fees for each block can be viewed online with any block explorer.
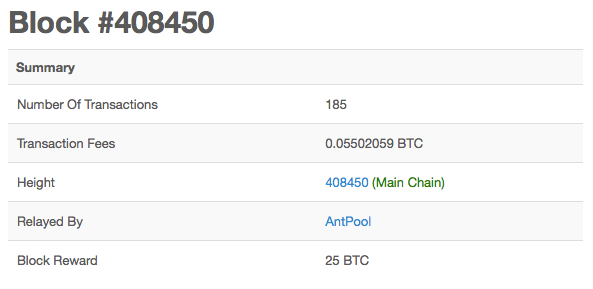
In the example above, we get information on block #408450:
- Number of transactions: Block #408450 contained 185 transactions.
- Transaction fees: There were 0.05502059 BTC worth of transaction fees in block #408450. The miner or mining pool (explained below) that mined this block receives the entirety of these fees.
- Height: Height is another name for block number. The first block mined was block #1 and is called the Genesis block.
- Relayed By: This block was successfully solved by Antpool, which is a Bitcoin mining pool.
- Block Reward: This block contained a 25 BTC reward, which is fully rewarded to the miner that relayed the block—in this case Antpool.
Bitcoin Mining™® © 2011-2021 Hesiod Services LLC | Terms | Privacy
Источник
What are you mining in bitcoin
Bitcoin mining is the process of adding transaction records to Bitcoin’s public ledger of past transactions or blockchain. This ledger of past transactions is called the block chain as it is a chain of blocks. The block chain serves to confirm transactions to the rest of the network as having taken place.
Bitcoin nodes use the block chain to distinguish legitimate Bitcoin transactions from attempts to re-spend coins that have already been spent elsewhere.
What is Bitcoin Mining?
What is the Blockchain?
Bitcoin mining is intentionally designed to be resource-intensive and difficult so that the number of blocks found each day by miners remains steady. Individual blocks must contain a proof of work to be considered valid. This proof of work is verified by other Bitcoin nodes each time they receive a block. Bitcoin uses the hashcash proof-of-work function.
The primary purpose of mining is to allow Bitcoin nodes to reach a secure, tamper-resistant consensus. Mining is also the mechanism used to introduce Bitcoins into the system: Miners are paid any transaction fees as well as a «subsidy» of newly created coins.
This both serves the purpose of disseminating new coins in a decentralized manner as well as motivating people to provide security for the system.
Bitcoin mining is so called because it resembles the mining of other commodities: it requires exertion and it slowly makes new currency available at a rate that resembles the rate at which commodities like gold are mined from the ground.
What is Proof of Work?
A proof of work is a piece of data which was difficult (costly, time-consuming) to produce so as to satisfy certain requirements. It must be trivial to check whether data satisfies said requirements.
Producing a proof of work can be a random process with low probability, so that a lot of trial and error is required on average before a valid proof of work is generated. Bitcoin uses the Hashcash proof of work.
What is Bitcoin Mining Difficulty?
The Computationally-Difficult Problem
Bitcoin mining a block is difficult because the SHA-256 hash of a block’s header must be lower than or equal to the target in order for the block to be accepted by the network.
This problem can be simplified for explanation purposes: The hash of a block must start with a certain number of zeros. The probability of calculating a hash that starts with many zeros is very low, therefore many attempts must be made. In order to generate a new hash each round, a nonce is incremented. See Proof of work for more information.
The Bitcoin Network Difficulty Metric
The Bitcoin mining network difficulty is the measure of how difficult it is to find a new block compared to the easiest it can ever be. It is recalculated every 2016 blocks to a value such that the previous 2016 blocks would have been generated in exactly two weeks had everyone been mining at this difficulty. This will yield, on average, one block every ten minutes.
As more miners join, the rate of block creation will go up. As the rate of block generation goes up, the difficulty rises to compensate which will push the rate of block creation back down. Any blocks released by malicious miners that do not meet the required difficulty target will simply be rejected by everyone on the network and thus will be worthless.
The Block Reward
When a block is discovered, the discoverer may award themselves a certain number of bitcoins, which is agreed-upon by everyone in the network. Currently this bounty is 25 bitcoins; this value will halve every 210,000 blocks. See Controlled Currency Supply.
Additionally, the miner is awarded the fees paid by users sending transactions. The fee is an incentive for the miner to include the transaction in their block. In the future, as the number of new bitcoins miners are allowed to create in each block dwindles, the fees will make up a much more important percentage of mining income.
Bitcoin Mining™® © 2011-2021 Hesiod Services LLC | Terms | Privacy
Источник
Bitcoin Mining Guide — Getting started with Bitcoin mining
Bitcoin mining is difficult to do profitably but if you try then this Bitcoin miner is probably a good shot.
How Bitcoin Mining Works
Before you start mining Bitcoin, it’s useful to understand what Bitcoin mining really means. Bitcoin mining is legal and is accomplished by running SHA256 double round hash verification processes in order to validate Bitcoin transactions and provide the requisite security for the public ledger of the Bitcoin network. The speed at which you mine Bitcoins is measured in hashes per second.
The Bitcoin network compensates Bitcoin miners for their effort by releasing bitcoin to those who contribute the needed computational power. This comes in the form of both newly issued bitcoins and from the transaction fees included in the transactions validated when mining bitcoins. The more computing power you contribute then the greater your share of the reward.
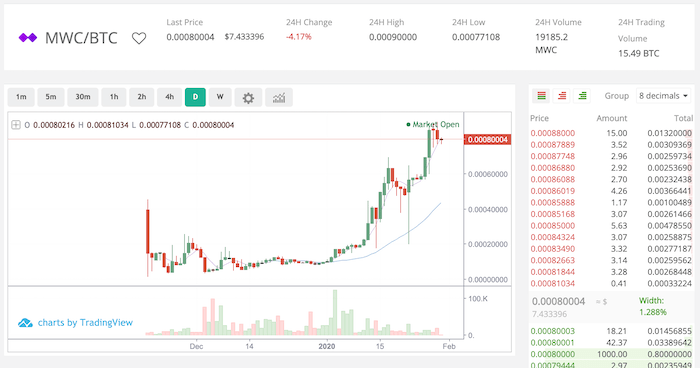
Sometimes you may want to mine a more volatile altcoin like MWC which is superior for scalability, privacy, anonymity and fungibility by utilizing MimbleWimble in the base layer.
With mainnet launching in November 2019 it has risen from $0.22 to over $8.00 in its first two months.
Step 1 — Get The Best Bitcoin Mining Hardware
Purchasing Bitcoins — In some cases, you may need to purchase mining hardware with bitcoins. Today, you can purchase most hardware on Amazon. You also may want to check the bitcoin charts.
How To Start Bitcoin Mining
To begin mining bitcoins, you’ll need to acquire bitcoin mining hardware. In the early days of bitcoin, it was possible to mine with your computer CPU or high speed video processor card. Today that’s no longer possible. Custom Bitcoin ASIC chips offer performance up to 100x the capability of older systems have come to dominate the Bitcoin mining industry.
Bitcoin mining with anything less will consume more in electricity than you are likely to earn. It’s essential to mine bitcoins with the best bitcoin mining hardware built specifically for that purpose. Several companies such as Avalon offer excellent systems built specifically for bitcoin mining.
Best Bitcoin Cloud Mining Services
Another option is to purchase in Bitcoin cloud mining contracts. This greatly simplifies the process but increases risk because you do not control the actual physical hardware.
Being listed in this section is NOT an endorsement of these services. There have been a tremendous amount of Bitcoin cloud mining scams.
Hashflare Review: Hashflare offers SHA-256 mining contracts and more profitable SHA-256 coins can be mined while automatic payouts are still in BTC. Customers must purchase at least 10 GH/s.
Genesis Mining Review: Genesis Mining is the largest Bitcoin and scrypt cloud mining provider. Genesis Mining offers three Bitcoin cloud mining plans that are reasonably priced. Zcash mining contracts are also available.
Hashing 24 Review: Hashing24 has been involved with Bitcoin mining since 2012. They have facilities in Iceland and Georgia. They use modern ASIC chips from BitFury deliver the maximum performance and efficiency possible.
Minex Review: Minex is an innovative aggregator of blockchain projects presented in an economic simulation game format. Users purchase Cloudpacks which can then be used to build an index from pre-picked sets of cloud mining farms, lotteries, casinos, real-world markets and much more.
Minergate Review: Offers both pool and merged mining and cloud mining services for Bitcoin.
Hashnest Review: Hashnest is operated by Bitmain, the producer of the Antminer line of Bitcoin miners. HashNest currently has over 600 Antminer S7s for rent. You can view the most up-to-date pricing and availability on Hashnest’s website. At the time of writing one Antminer S7’s hash rate can be rented for $1,200.
Bitcoin Cloud Mining Review: Currently all Bitcoin Cloud Mining contracts are sold out.
NiceHash Review: NiceHash is unique in that it uses an orderbook to match mining contract buyers and sellers. Check its website for up-to-date prices.
Eobot Review: Start cloud mining Bitcoin with as little as $10. Eobot claims customers can break even in 14 months.
MineOnCloud Review: MineOnCloud currently has about 35 TH/s of mining equipment for rent in the cloud. Some miners available for rent include AntMiner S4s and S5s.
Bitcoin Mining Hardware Comparison
Currently, based on (1) price per hash and (2) electrical efficiency the best Bitcoin miner options are:
Источник