Линейно-временная функция (Ramp)
Для управления переменной (уставка SP), задающей значение технологического процесса, по закону линейно-нарастающей функции используется функциональный блок Ramp. Данная задача востребована часто при процессах нагрева или охлаждения для различных инертных процессах (крупные печи, научные внедрения, пищевая промышленность).
Обрабатывает входные значения технологического процесса и формирует выходной аналоговый сигнал, который является уставкой для работы конкретного регулятора. Линейно-нарастающая функция предназначена для растянутого во времени достижения заданной уставки технологическим процессом. Разрядность процесса прироста или замедления зависит от быстродействия процессора (скважности), чем выше разрядность, тем с большей точностью (ровнее линия) будет вестись процесс.
Блок поддерживает возможность временного прекращения набора/снижения линейно-нарастающей функции в зависимости от потребности технологического процесса (например, при отсутствии необходимости регулирования).
Логика работы функционального блока позволяет добиться достижения плавающей уставки (FSP) до статической уставки (SP) за заданное (RAMP_TIME) время. Данное замедление регулированием технологического процесса требуется для инерционных процессов.


Назначение входов и выходов функционального блока
| Входы: | Тип | Описание | Выходы: | Тип | Описание |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| START | BOOL | Разрешение для начала расчёта | OUT | REAL | Выход плавающей уставки на регулятор |
| SP | REAL | Значение статической уставки | FSP_SP | BOOL | Выход равен статической уставке |
| PV | REAL | Значение измеряющей переменной процесса | FSP_PV | BOOL | Выход равен измеряемому значению |
| RAMP_TIME | TIME | Заданное время | |||
| INDIRECT | BOOL | Направление наклона прямой |
Особенности применения
Угол наклона линейно-нарастающей функции при первоначальном воздействии (START) происходит по времени (RAMP_TIME), все последующие скачки статической уставки (SP) происходят по скорости один градус в минуту.
Рекомендации по применению

Выход с функционального блока служит уставкой для регулятора. Переменные FSP_SP FSP_PV, обеспечивают визуализацию присвоенных в теле блока значений выходу. FSP_SP присваивается в случае если измеряющая процесса перешла границу SP, а FSP_PV если на вход блока START присваивается значение FALSE. Если переменная INDIRECT активирована (TRUE), то меняется геометрическое расположение угла наклона FSP на противоположное и функция. От выбора значения этого входа зависит характер работы блока линейно-нарастающий или линейно-убывающей функци
Источник
Ramp Rate
Related terms:
Download as PDF
About this page
Flexible active power control of PV systems
6.5 Power ramp-rate control (PRRC)
The power ramp-rate control (PRRC) strategy is employed to limit the fluctuation rate in the PV output power under dynamically changing irradiance conditions (e.g., passing clouds). In this operation mode, the PV output power is controlled in a ramp-changing manner in order to limit its change rate to a certain value R r ⁎ [41] . Clearly, to achieve the PRRC, the change rate of the PV output power R(t) should be continuously measured, which can be calculated as
where Δ ppv is the power difference measured in the time period of Δt. Notably, the measuring window (i.e., Δt ) of the ramp rate can also affect the performance of the PRRC strategy. This is mainly because the operating point of the PV system usually oscillates in steady state due to the MPP searching (e.g., the P&O MPPT algorithm). Therefore, the measured ramp rate of the PV power will not be zero even under a constant solar irradiance condition. In prior-art solutions, a moving average or a low-pass filter is usually employed to reduce the power oscillation [14] , [42] and to improve the measurement. In this regard, the ramp-rate measurement is a challenge issue when implementing the PRRC.
The measured ramp rate calculated by Eq. (6.12) is the key to determining the operating mode of the PV system. More specifically, as long as the ramp rate of the PV power R(t) is below the ramp-rate limit R r ⁎ (e.g., under slow changing irradiance conditions), the MPPT operation can be employed, and the PV system delivers the maximum available power to the grid. This is demonstrated by the operation trajectory from A to B in the PV array characteristic in Fig. 6.26 . However, once the measured ramp rate exceeds the limit, the PV output power should be reduced from the maximum available value (e.g., power curtailment) in a way to lower the change rate and then follow the ramp-rate profile. This can be achieved by perturbing the operating point of the PV system away from the MPP, as it is illustrated by the operating trajectory from B to C in Fig. 6.26 . In this operation, the PV system will operate in the PLC mode with a dynamically changing power limit calculated according to the ramp rate. The PV voltage reference with the PRRC can be summarized as
Fig. 6.26 . Operational principle of the power ramp-rate control (PRRC) algorithm: MPPT mode (A → B) and PRRC mode (B → C), where R1 = (Pmpp1 − Pmpp2)/t1 and R2 = (Pmpp2 − Pmpp3)/t2 are the PV power ramp rates and R r ⁎ is the ramp-rate limit.
with v mpp ⁎ being the reference voltage from an MPPT algorithm (e.g., P&O MPPT) and vstep is the perturbation step size.
The performance of the PRRC strategy is demonstrated by employing two trapezoidal solar irradiance profiles with different slopes to emulate different changing solar irradiance conditions. First, the PRRC strategy is demonstrated with the slow changing solar irradiance condition in Fig. 6.27 A, where two different ramp-rate limits of R r ⁎ = 10 and 20 W/s are employed. It can be seen from Fig. 6.27 A that the PV power is in the ramp-changing manner when the solar irradiance increases (i.e., the PV power increases). The corresponding ramp rate is measured in Fig. 6.28 A, indicating that the PRRC strategy can limit the ramp rate of the PV power. Similar performance can also be observed in the case of fast changing solar irradiance condition in Fig. 6.27 B. In this case, it is more challenging for the PRRC strategy to limit the ramp rate, where it can be seen in Fig. 6.28 B that the instantaneous power ramp rate R(t) exceeds the limit temporarily during a transient (e.g., rapid increase of solar irradiance level). Nonetheless, the change rate can still be limited with the PRRC strategy.
Fig. 6.27 . Performance of the PRRC strategy with different ramp-rate limits under: (A) a slowly changing and (B) a fast changing irradiance condition.
Fig. 6.28 . Measured ramp rate of the PRRC strategy with different ramp-rate limits under (A) a slowly changing and (B) a fast changing irradiance condition.
Furthermore, the test with two daily real-field solar irradiance profiles (a clear day and a cloudy day) is also carried out (with an acceleration from 24 h to 24 min) where the ramp-rate limit of R r ⁎ = 10 W / s is adopted. The experimental results are shown in Figs. 6.29 and 6.30 . Under the clear-day condition, the solar irradiance changes with a slow and smooth transition, as it can be seen from the available power in Fig. 6.29 A. The ramp rate of the PV power can be accurately controlled with the PRRC strategy as it can be observed from the PV output power and the corresponding ramp rate in Figs. 6.29 A and 6.30 A, respectively. However, when the cloudy day profile is adopted, the ramp rate is difficult to control, as shown in Fig. 6.29 B. It can be seen that although the PV output power is controlled in a ramp-changing manner, it presents variations, as observed in Fig. 6.30 B. Notably, there is a short period, where the ramp-rate limit is violated due to the very fast dynamics in the solar irradiance. In that case, the algorithm requires a certain iteration (sample periods) to reduce the PV power following the ramp-rate demand. Nevertheless, the results have demonstrated the effectiveness of the PRRC strategy that can be applied to various operating conditions. Moreover, it is worth to be mentioned that the PRRC algorithm can only reduce the ramp rate during the increasing solar irradiance condition (i.e., power ramp up). During the fast decreasing in the solar irradiance, the PV system needs to provide extra power (higher than the available power) in order to maintain the ramp-down rate, which fundamentally cannot be achieved by the power curtailment (i.e., the FPPT control). A possible solution to this situation is to cooperate with the forecasting method to predict the ramp-down incident and thus reduce the PV power slightly before it occurs as proposed in [43] . Clearly, the above experimental tests verified that the ramp-up rate of the PV power could be limited when the PRRC is enabled.
Fig. 6.29 . Performance of the PRRC strategy with the ramp-rate limit of 10 W/s under two daily operation profiles: (A) a clear day and (B) a cloudy day.
Fig. 6.30 . Measured ramp rate of the PRRC strategy with the ramp-rate limit of 10 W/s under two daily operation profiles: (A) a clear day and (B) a cloudy day.
Источник
ramp rate
Earres
Senior Member
Field and topic:
Speed of a machine
———————
Sample sentence:
Start up the machine (up to max. running speed 3000 rpm at a ramp rate of 3000 rpm/minute).
********************
Hi! I´m looking for a good translation of the term «ramp rate». I´ve tried with «índice de aumento» but I´m not sure. Could you please clarify the meaning and suggest a proper term in Spanish?
begoña fernandez
Senior Member
Field and topic:
Speed of a machine
———————
Sample sentence:
Start up the machine (up to max. running speed 3000 rpm at a ramp rate of 3000 rpm/minute).
********************
Hi! I´m looking for a good translation of the term «ramp rate». I´ve tried with «índice de aumento» but I´m not sure. Could you please clarify the meaning and suggest a proper term in Spanish?
cacalos
Member
Senior Member
My spanish software collegues tell me ‘Pendiente de rampa’.
‘Acceleration’ is mostly used to describe the result of force vs. mass or torque vs. rotational inertia.
‘Ramp up’ is used in control system programming where the speed of the components is controlled by a computer. Changing the speed at a certain rate, the ramp rate, of course results in an acceleration, but the ramp rate is programmed in the software so it is not a wild shooting against the max. value.
In this example it is controlled to increase at a rate of 3000 RPM/min which increases the speed with 50 RPM every second and you can typically change this rate by turning a knob or changing parameters in the program. Uncontrolled and without a ramp function the complete acceleration phase 0-3000 RPM would have been over in less than one second. (I suppose we are dealing with a relatively small electric motor with a max. speed of 3000 RPM).
I know it’s a very technical explanation , but so is this stuff, and I hope you get a little out of it.
NSV
Earres
Senior Member
cacalos
Member
My spanish software collegues tell me ‘Pendiente de rampa’.
‘Acceleration’ is mostly used to describe the result of force vs. mass or torque vs. rotational inertia.
‘Ramp up’ is used in control system programming where the speed of the components is controlled by a computer. Changing the speed at a certain rate, the ramp rate, of course results in an acceleration, but the ramp rate is programmed in the software so it is not a wild shooting against the max. value.
In this example it is controlled to increase at a rate of 3000 RPM/min which increases the speed with 50 RPM every second and you can typically change this rate by turning a knob or changing parameters in the program. Uncontrolled and without a ramp function the complete acceleration phase 0-3000 RPM would have been over in less than one second. (I suppose we are dealing with a relatively small electric motor with a max. speed of 3000 RPM).
I know it’s a very technical explanation , but so is this stuff, and I hope you get a little out of it.
NSV
Источник
Функции/алгоритмы/опции.
Функции/алгоритмы/опции.

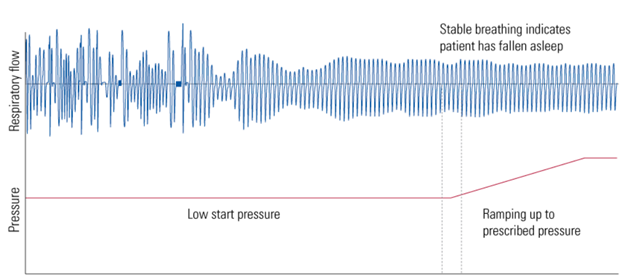
Иногда очень сложно разобраться во всех этих названиях различных сипап-аппаратов для терапии обструктивного апноэ сна. Сегодня мы разберем один из новых алгоритмов аппарата AirSense 10 AutoSet, ResMed — AutoRamp.
Что же это такое?
Многие СИПАП-аппараты разных производителей оснащены так называемой опцией «Ramp Time» (отложенный старт терапии) — это период постепенного повышения давления от низкого начального до величины, применяемый при лечении. Данная функция позволяет пациентам облегчить начало терапевтического сеанса, постепенно увеличивая давление, чтобы помочь вам быстрее заснуть.
Обычно, Ramp Time устанавливается на определенный период времени (от 0 до 45 минут). Но, кто сказал, что вы должны заснуть именно через 20 или 45 минут? А если вам достаточно и 15 минут?
Алгоритм AutoRamp компании ResMed – это еще один инновационный шаг вперед для вашего комфортного сна. Аппарат модели AirSense 10 AutoSet может похвастаться технологией AutoRamp.
AutoRamp — это интеллектуальное обнаружение наступления сна : аппарат самостоятельно распознает когда пользователь бодрствует или спит.
Больше не нужно нажимать кнопки, чтобы активировать функцию Ramp Time, потому что AutoRamp с функцией Sleep Onset Detection (обнаружение сна) сделает эту работу за вас! AutoRamp предназначен для того, чтобы сделать сипап-терапию максимально комфортной с момента включения аппарата.
- Благодаря данной технологии Вы легко и непринужденно засыпаете. Терапия апноэ сна начинается с обеспечения низкого начального давления, которое поможет вам легко заснуть. Затем, используя функцию обнаружения начала сна, аппарат плавно увеличивает давление до необходимого, когда обнаруживает, что вы заснули.
- В отличие от, так сказать, традиционной функции Ramp Time, которая после завершения установленного периода отсрочки набора давления (от 0 до 45 минут) сразу начинает повышать давление, технология AutoRamp не увеличивает давление до тех пор, пока не определит, что вы заснули.
- AutoRamp доступна только на новой серии аппаратов ResMed — AirSense 10 AutoSet.
Как технология AutoRamp помогает вашему прибору «узнать» когда вы заснули?
Ваше устройство AirSense 10 AutoSet будет знать, что вы заснули не более трех минут спустя. Когда вы включаете аппарат, AutoRamp «ищет» три признака:
а) 30 стабильных дыханий (примерно 3 минуты)
б) 5 последовательных дыханий с храпом
в) 3 эпизода обструктивных апноэ или гипопноэ в течение 2 минут
Как только появляется какой-либо из этих признаков, AutoRamp медленно и комфортно увеличивает давление до тех пор, пока не достигнет предписанного уровня.
Кроме того, независимо от того, когда вы засыпаете, AutoRamp гарантирует, что вы достигнете предписанного давления не позднее, чем через 30 минут после включения аппарата. Это гарантия того, что вы получите эффективное лечение апноэ во сне. Основываясь на исследованиях, большинство людей, получающих СИПАП-терапию, засыпают через 20–25 минут.
Благодаря низкому давлению во время бодрствования и устойчивому и комфортному увеличению, алгоритм AutoRamp — одна из многих новых функций СИПАП-аппарата AirSense 10 AutoSet, ResMed разработанная для повышения комфорта лечения.
Источник