- Обратный отсчет до халвинга биткоина
- What Is a Bitcoin Halving?
- Why Are Halvings Significant?
- How Many Bitcoin Halvings Have There Been Before?
- How Is Our Timer Calculated?
- Bitcoin Block Reward Halving Countdown
- What is a block halving event?
- Why was this done?
- Predictable monetary supply
- Who controls the issuance of Bitcoin?
- Past halving event dates
- Past halving price performance
- How to buy Bitcoin?
- Обратный отсчет до халвинга Биткоина
- Что такое халвинг?
- Почему халвинг важен?
- Сколько халвингов Биткоина уже состоялось?
- Как работает халвинг Биткоин блоков?
- Как рассчитывается наш таймер?
- BITCOIN HALVING
- Miners, transaction fees and the block reward
- What are the implications of a block reward halving?
- What do you think?
Обратный отсчет до халвинга биткоина
What Is a Bitcoin Halving?
In all their infinite wisdom, Bitcoin’s anonymous inventor Satoshi Nakamoto decided that only 21 million BTC would ever exist. They wanted new coins to be released gradually into the market — but at the same time, it was crucial for a generous supply of Bitcoin to start circulating sooner rather than later.
New BTC are given to Bitcoin miners as their Bitcoin block reward when they verify blocks of transactions. To begin with, the reward stood at 50 BTC per block. This would have been worth under a dollar back in 2009 — but at today’s rates (April 28), the price of Bitcoin would’ve gotten you a windfall of around $388,000.
Such generous terms wouldn’t last forever. Under Bitcoin’s rules, rewards would only stay this high for the first 210,000 blocks, and then they would be cut by 50%. By this point, half of the BTC that would ever exist — 10.5 million — were out in circulation.
For this upcoming Bitcoin halving (also known as halvening), the total number of Bitcoin mined by miners per block will be reduced from 6.25 BTC to 3.125 BTC.
Why Are Halvings Significant?
As rare as an eclipse, a World Cup and your best friend buying you a drink, the Bitcoin halving generates a lot of excitement in crypto circles. They are at the very core of the cryptocurrency’s economic models, because they ensure that coins will be issued at a steady pace, following a predictable decaying rate.
This controlled rate of monetary inflation is one of the main differences between most cryptocurrencies and traditional fiat currencies, which essentially have an infinite supply due to the monetary policy of central banks.
There will only ever be 32 Bitcoin halving events. Once the 32nd halving is completed, there will be no more new Bitcoin created, as its maximum supply of 21 million will have been reached.
If you’re interested in acquiring some Bitcoin yourself before the halving, see here for everything you need to know about the purchasing process.
How Many Bitcoin Halvings Have There Been Before?
The first-ever Bitcoin halving took place on Nov. 28, 2012 — slashing rewards to just 25 BTC. On this date, a single BTC would set you back about $12. But just look at where it was a year later. Dusting off the CMC archives, we can see that the price of Bitcoin stood at $1,031.95 on that date in 2013. That’s an annual rise of 8,500%, the types of returns that would cause most Wall Street investors to faint.
Let’s travel in time to the second halving in 2016, when rewards were about to tumble once again, this time to 12.5 BTC. On the date Bitcoin hit 420,000 blocks — July 9, to be exact — one coin cost $650.96. A year later, Bitcoin was already at $2,518.44. However, the real rise took place 5 months later, when on Dec. 17, 2017, Bitcoin ballooned to its all-time high of $20,089. It took just 526 days for growth of 2,990% to be realized.
It’s fair to say that the jury is still out on whether this upcoming halving will be followed by the type of growth that followed the previous halvings. Either way, it’ll take 12 to 18 months to know if Bitcoin can pull it off again.
How Is Our Timer Calculated?
You may notice our countdown has a different estimation than other Bitcoin halving countdowns, and the obvious question is, «»Why?»»
Instead of using the commonly quoted average Bitcoin block time (10 minutes), we are using live blockchain statistics to obtain an estimation of the current average Bitcoin block time, and then using this number for our calculations. We believe that this makes our countdown more accurate, and any fluctuations that you may see speak to the precision of our way of measurement.
The Bitcoin Halving timer on CoinMarketCap is calculated using the following formula:
Источник
Bitcoin Block Reward Halving Countdown
What is a block halving event?
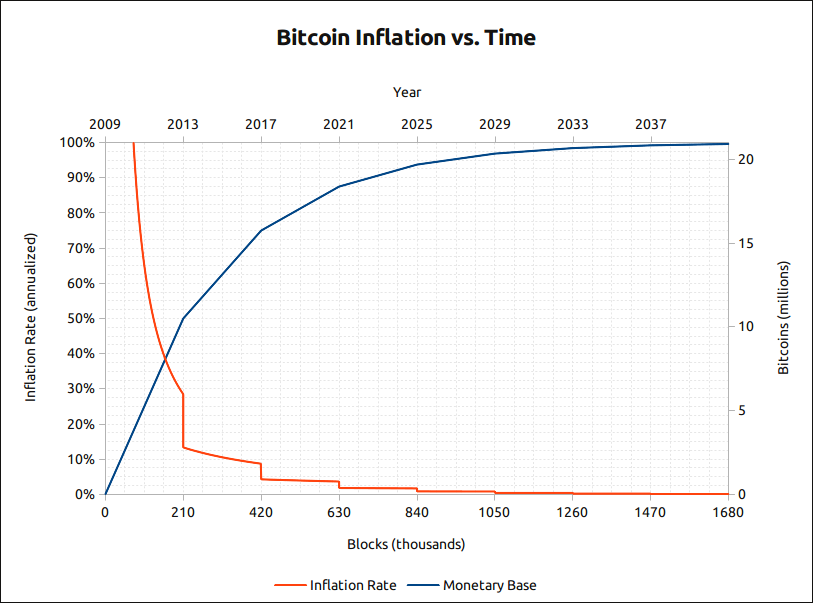
As part of Bitcoin’s coin issuance, miners are rewarded a certain amount of bitcoins whenever a block is produced (approximately every 10 minutes). When Bitcoin first started, 50 Bitcoins per block were given as a reward to miners. After every 210,000 blocks are mined (approximately every 4 years), the block reward halves and will keep on halving until the block reward per block becomes 0 (approximately by year 2140). As of now, the block reward is 6.25 coins per block and will decrease to 3.125 coins per block post halving.
Why was this done?
Bitcoin was designed as a deflationary currency. Like gold, the premise is that over time, the issuance of bitcoins will decrease and thus become scarcer over time. As bitcoins become scarcer and if demand for them increases over time, Bitcoin can be used as a hedge against inflation as the price, guided by price equilibrium is bound to increase. On the flip side, fiat currencies (like the US dollar), inflate over time as its monetary supply increases, leading to a decrease in purchasing power. This is known as monetary debasement by inflation. A simple example would be to compare housing prices decades ago to now and you’ll notice that they’ve increased over time!
Predictable monetary supply
Since we know Bitcoin’s issuance over time, people can rely on programmed/controlled supply. This is helpful to understand what the current inflation rate of Bitcoin is, what the future inflation rate will be at a specific point in time, how many Bitcoins are in circulation and how many remain left to be mined.
Who controls the issuance of Bitcoin?
The network itself controls the issuance of Bitcoins, derived by consensus through all Bitcoin participants. Ever since Bitcoin was first designed, the following consensus rules exist to this day:
- 21,000,000 Bitcoins to ever be produced
- Target of 10-minute block intervals
- Halving event occurring every 210,000 blocks (approximately every 4 years)
- Block reward which starts at 50 and halves continually every halving event until it reaches 0 (approximately by year 2140)
Any change to these parameters requires all Bitcoin participants to agree by consensus to approve the change.
Past halving event dates
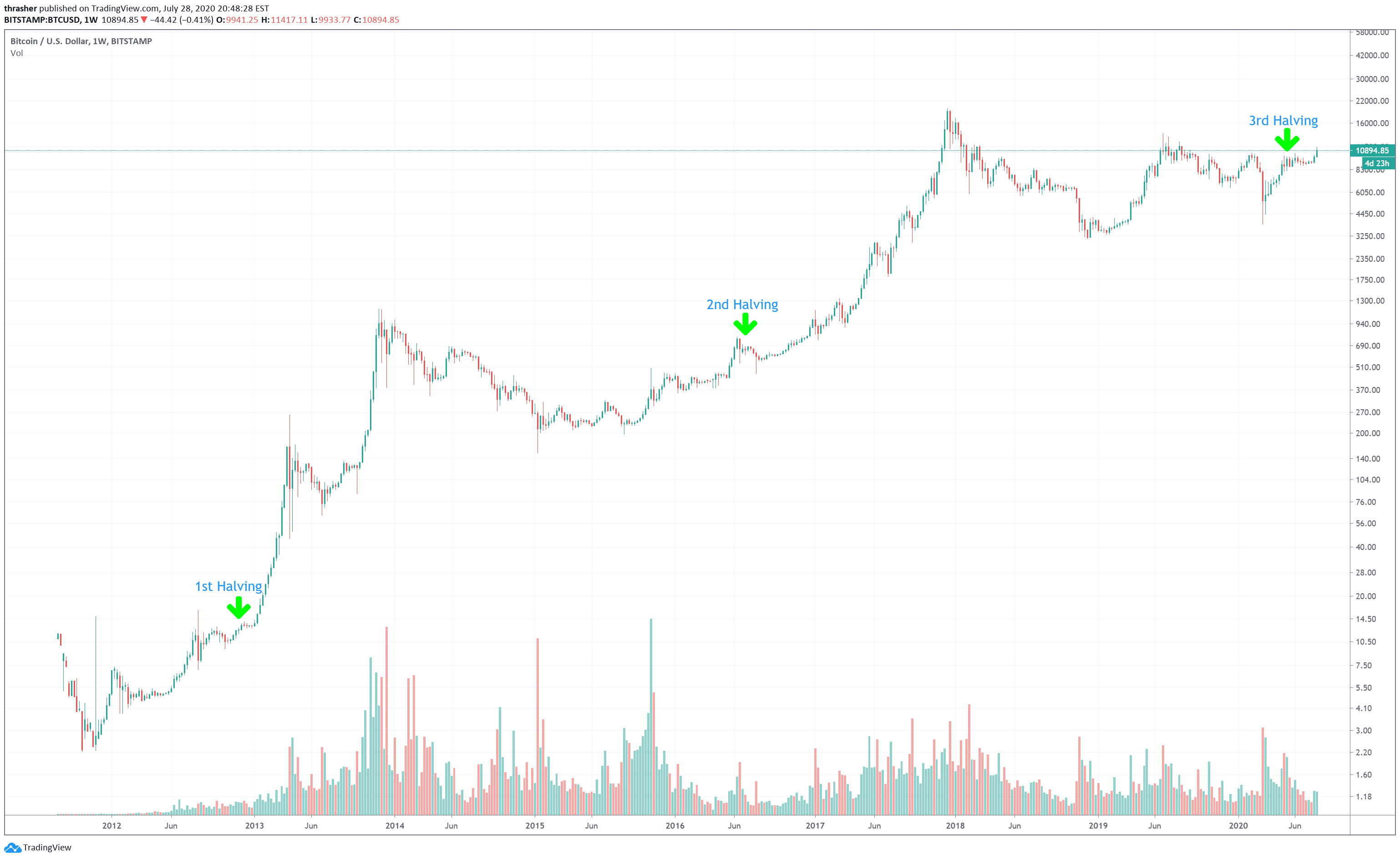
- The first halving event occurred on the 28th of November, 2012 (UTC) at block height 210,000
- The second halving event occurred on the 9th of July, 2016 (UTC) at block height 420,000
- The third halving event occurred on the 11th of May, 2020 (UTC) at block height 630,000
Past halving price performance
It is always a debate on what Bitcoin will do in terms of pricing for a halving event. Some people believe that the halving is already priced in by the market and thus there’s no expectation for the price to do anything. Others believe that due to price equilibrium, a halving of supply should cause an increase in price if demand for Bitcoins is equal or greater than what it was before the halving event. Below is a chart showing past price performance of the two halving events:
How to buy Bitcoin?
Coinbase is one of the largest cryptocurrency exchange in the world, serving over 102 countries, 30 million+ customers and over 150 billion in trading volume. Funds are protected by insurance and secure storage. You can also earn up to $158 worth of cryptocurrencies. Click below to find out more:
Источник
Обратный отсчет до халвинга Биткоина
Что такое халвинг?
Халвинг — это процесс уменьшения скорости генерирования новых единиц криптовалюты. В частности, это относится к периодически происходящему событию, последствием которого является уменьшение награды майнеров за успешно добытый блок.
Почему халвинг важен?
Халвинг является неотъемлемой частью экономической модели криптовалют, поскольку он отвечает за стабильный темп создания новых монет и его дальнейшее регулирование. Такой контролируемый уровень денежной инфляции является одним из основных различий между криптовалютами и традиционными фиатными валютами, которые, по сути, имеют бесконечное циркулирующее предложение.
Сколько халвингов Биткоина уже состоялось?
По состоянию на июль 2019 состоялось только два халвинга. Это произошло 28 ноября 2012 года и 9 июля 2016 года. Во время первого халвинга цена за один биткоин составляла 12.31$, а во время второго аналогичного события стоимость монеты была на отметке в 650.63$.
Всего запланировано 32 халвинга. После того, как все они произойдут, создание новых биткоинов будет невозможным, таким образом достигается максимальное предложение монет.
| Халвинг | Ожид. Дата | Высота блока | Награда за блок (BTC) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Нет данных | 0 | 50 |
| 1 | 11/28/2012 | 210,000 | 25 |
| 2 | 07/09/2016 | 420,000 | 12.5 |
| 3 | 2020 | 630,000 | 6.25 |
| 4 | 2024 | 840,000 | 3.125 |
| 5 | 2028 | 1,050,000 | 1.5625 |
Как работает халвинг Биткоин блоков?
Халвинг Биткоина является важной функцией в протоколе монеты. Код можно найти на Bitcoin Core Github, а ниже приведен фрагмент кода, который делает возможным халвинг Биткоина. В нем указано, что награда за блок будет уменьшаться вдвое каждые 210 000 блоков.
Как рассчитывается наш таймер?
Вы можете заметить, что наш обратный отсчет халвинга биткоина несколько отличается от остальных, возможно вы зададитесь вопросом: «Почему так?»
Все дело в том, что для более точной работы таймера, мы осуществляем расчеты на основе реального времени формирования блока, вместо того, чтобы использовать среднее значение (10 мин). Хоть оставшееся время на нашем таймере может иногда видоизменятся, мы считает, что оно является самым точным.
Таймер халвинга биткоина в Binance Academy рассчитывается по следующей формуле:
(Халвинг блок — высота следующего блока) * среднее время между блоками — предположительное время добычи следующего блока.
Посетите наш глоссарий для дальнейшего ознакомления с халвингом.
Источник
BITCOIN HALVING
Have you always wondered what the Bitcoin Halving buzz is all about? We are here to give you a detailed explanation of everything you need to know.
Miners, transaction fees and the block reward
In public blockchain networks miners verify transactions in blocks and are rewarded with transaction fees and newly minted coins. Transactions waiting to be processed are temporarily stored in the mempool
The number of transactions that fit in a block is fixed by something called a blocksize. Miners will thus process transactions with the highest transaction fees first to optimize their income. On our Bitcoin Mempool dashboard, you can filter the transactions in the mempool by fee per kilobyte and on transaction pages of transactions that are waiting to be processed, we state the priority of processing. The lower is the number on the left, the faster the transaction gets into a block.
On the Bitcoin network, a block is limited to 1.3 MB, good for close to 3500 transactions. On the Bitcoin Cash network, the block limit is 32 MB but often not fully utilized. Information about the number of transactions in a Bitcoin Cash block can be found here.
Besides transaction fees, miners also receive block rewards for every block that they process correctly. The first transaction that a miner processes in a block, has new Bitcoin sent to the miner. This is called a ‘Coinbase transaction’. Besides the block reward, a Coinbase transaction also includes the transaction fees attached to transactions that are included in the block. An example of a Coinbase transaction can be found here.
In Bitcoin and several other blockchains, the number of newly minted coins per block is cut in half after every 210,000 blocks. This means that inflation is limited, as the number of new bitcoins coming into circulation will eventually go to zero. As every block is processed at a target rate of 10 minutes, block reward halvings happen approximately every 4 years. In Bitcoin networks, the block reward started at 50 BTC per block, which already has been halved 2 times to 12.5 BTC per block now. Soon, this will become 6.25 BTC per block. In, approximately, the year 2140 there will be 21 million BTC in circulation. We can see this in the following graph:
To find out how many bitcoins are currently in circulation, you can check out this chart here.
What are the implications of a block reward halving?
There are 2 main implications to be thought of. The first one is that the price of bitcoin may increase. The second one is that the security of the network may go down if the price does not increase.
Referring to classical economic theory, many people think that the price of bitcoin should increase, due to the reduced supply of bitcoins to the market:
At the moment, miners are rewarded with approximately 1800 new bitcoins per day. With a price of $6,646.- this means a daily reward of $11,962,800.
Miners use tons of electricity to process transactions, and the general assumption is that miners directly sell their newly minted bitcoins in order to cover their costs. This would mean that after the halving not 1800 bitcoins, but only 900 bitcoins are freshly supplied to the market every day. This scarcity is believed to have a positive effect on the bitcoin price.
If the price of bitcoin does not increase after the block reward halving, the revenue of miners calculated in $USD will decrease. This means that they will have problems covering their cost, and this will drive miners with the highest electricity costs out of the market first. The reduction in electricity consumption to maintain the network means that the difficulty of processing a block of transactions will drop. Theoretically, this means that it would be easier to attack the blockchain network and create 51% attacks.
What do you think?
To stay up-to-date on the latest developments of the Bitcoin halving and for ongoing discussion, please follow us on Twitter or join our Telegram group!
Источник






