- Send and receive BTC/LTC — difference between SegWit and Legacy address
- For BTC:
- For LTC:
- What is the difference between SegWit and Legacy address?
- Why use SegWit?
- Why can’t I send BTC/LTC from my external legacy address to Crypto.com DeFi Wallet?
- Что такое SegWit в криптовалютах и для чего он нужен
- Что такое SegWit ?
- SegWit представила новую концепцию – «вес блока»
- Преимущества протокола Сегвит:
- Поддержка протоколов второго уровня
- Не все счастливы
- Перспективы SegWit
- Litecoin (LTC)
- 1. What is Litecoin (LTC)?
- 2. Litecoin’s key features
- Segregated Witness (shared with Bitcoin)
- Lightning Network (shared with Bitcoin)
- MimbleWimble as a privacy feature (in implementation)
- 3. Economics and supply distribution
- 4. Project team
Send and receive BTC/LTC — difference between SegWit and Legacy address
Crypto.com DeFi Wallet currently supports sending BTC/LTC with SegWit address. As for receiving BTC/LTC into your SegWit wallet, you may send BTC/LTC from your Legacy or SegWit address — as long as your current wallet supports sending to SegWit.
For BTC:
Legacy (P2PKH): addresses start with a 1
Nested SegWit (P2SH): addresses start with a 3
Native SegWit (bech32): addresses start with bc1
For LTC:
Legacy: addresses start with a L
SegWit (P2SH): addresses start with a 3 or M
Please note that if you have imported an external wallet on Crypto.com DeFi Wallet with Legacy BTC/LTC addresses, unfortunately the legacy balances will not be displayed on the Crypto.com DeFi Wallet.
What is the difference between SegWit and Legacy address?
Legacy address is the original BTC address while SegWit is the newer address format with lower fees.
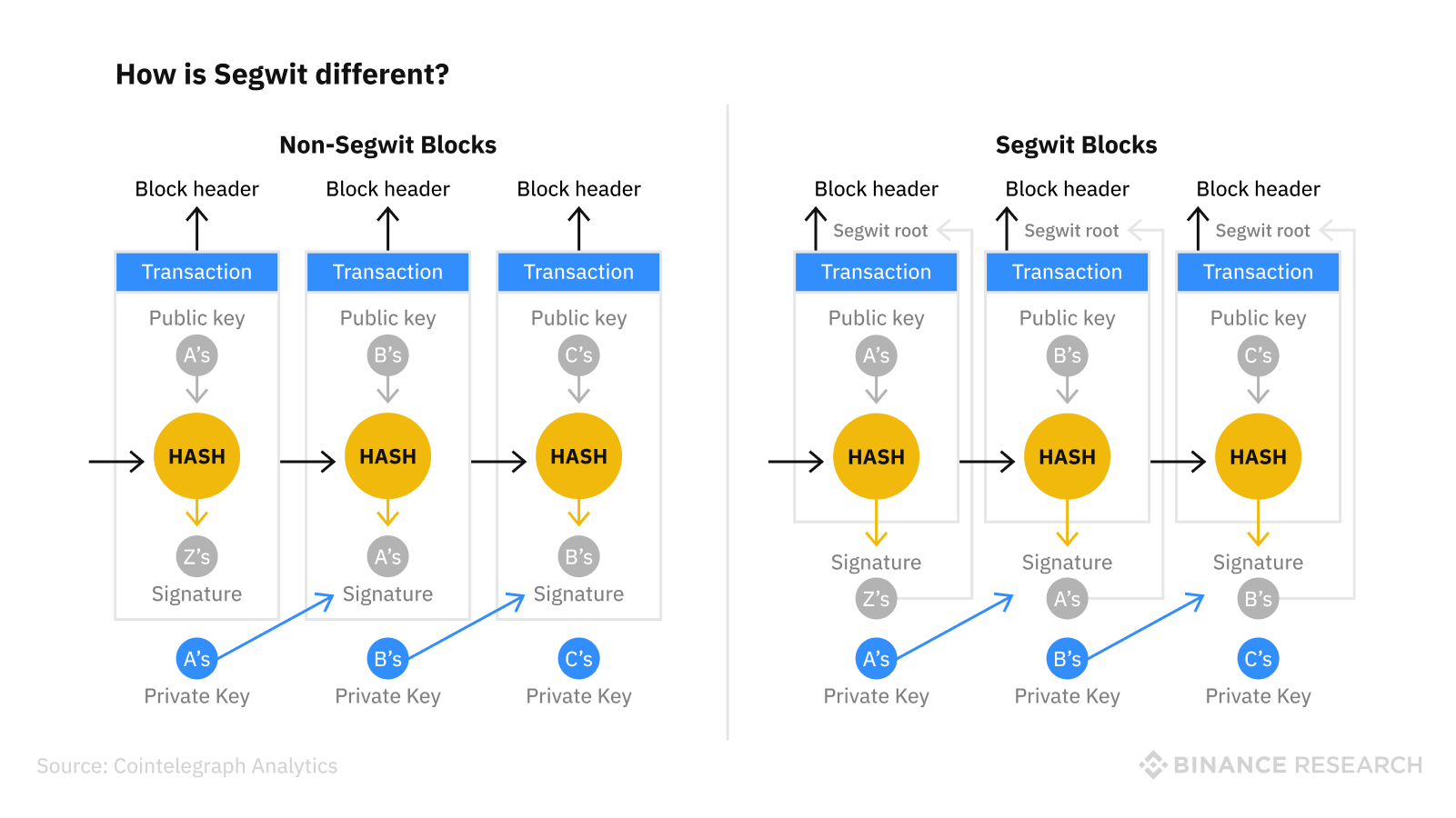
SegWit means Segregated Witness, where Segregated is to separate and Witness is the transaction signatures involved with a specific transaction. In a nutshell, it is an improvement over the current bitcoin blockchain which reduces the size needed to store transactions in a block.
Why use SegWit?
The main benefit of separating the transaction signature from the transaction data is it reduces the size of the transaction data needed to store in one block. This allows each block to have extra capacity to store more transactions per block. This means the network can process more transactions per block and the sender pays lower transaction fees. This helps to improve your transaction confirmation lead time with added security.
Another advantage of SegWit is that they are backwards compatible, meaning that you are able to send funds from a SegWit address to a Legacy address.
Why can’t I send BTC/LTC from my external legacy address to Crypto.com DeFi Wallet?
One major downside with a SegWit address is that not all wallets, exchanges and services support sending to them. You will need to make sure that whatever you are using to send to your Crypto.com DeFi Wallet SegWit address understands the Segwit address.
If you see invalid BTC/LTC address error on where you’re initiating the send, it’s very likely that the wallet does not support SegWit.
Источник
Что такое SegWit в криптовалютах и для чего он нужен
SegWit (сокращенная форма от Segregated Witness) – это обновление протокола Блокчейн, которое изменяет способ хранения данных. Простыми словами это способ, позволяющий ускорить пропускную способность сети Блокчейн, тем самым делая ее более привлекательной для оплаты товаров и услуг криптовалютой. Питер Вюлле – разработчик SegWit, впервые представил эту идею на конференции Scaling Bitcoin в декабре 2015 года. Затем SegWit был активирован на Litecoin 10 мая 2017 года, а 23 августа 2017 года – на Bitcoin.
Что такое SegWit ?
Многие приветствовали Сегвит, как долгожданное решение проблемы масштабирования Биткоина. Максимальный размер блока в основном протоколе составляет 1 МБ, что ограничивает количество транзакций, которые Биткоин может обрабатывать за секунду. Для примера, Visa обрабатывает 1000 транзакций за секунду, а Биткоин примерно 3. Это мешает Биткоину стать широко используемой платежной системой.
Хотя приложение SegWit делает возможным обработку большего количества транзакций в блоках Биткоина, первоначальная его цель состояла в том, чтобы исправить ошибку в коде Биткоина, называемую транзакционной податливостью. Этот недостаток позволял кому-либо изменять мелкие детали, которые трансформировали идентификатор транзакции (и последующий хеш), но не содержание. Хотя это и не является критичной проблемой для Биткоинов, но это препятствовало разработке более сложных функций, таких как протоколы второго уровня и интеллектуальные контракты.
Сегвит блокирует транзакционную податливость, удаляя информацию подписи (иначе известную как информация о свидетеле), и сохраняет ее за пределами базового блока транзакций. При этом подписи и скрипты могут быть изменены без влияния на идентификатор транзакции.
SegWit представила новую концепцию – «вес блока»
Дополнительное преимущество, которое приобретает гораздо большее значение, заключается в том, что, без информации подписи, транзакции весят значительно меньше. Это означает, что больше информации может вписываться в блок, а Биткоин может иметь большую пропускную способность.
Таким образом, SegWit не увеличивает ограничение размера блока, а позволяет включить больше транзакций в пределах блоков 1 МБ. Ключ 4MБ включает в себя отдельные данные свидетелей, которые технически не составляют часть базового блока транзакций 1 МБ.
Преимущества протокола Сегвит:
- Третье лицо не может изменить подпись транзакции. Это дает возможность внедрения новых смарт-контрактов.
- Увеличение пропускной способности сети Блокчейн, благодаря уменьшению размера транзакций. Количество информации, передаваемой во время транзакции, остается неизменным. Это возможно из-за перемещения подписи данных за пределы блока.
- Снижение начисления комиссионных сборов. Из-за роста количества обрабатываемых транзакций за секунду, они станут дешевле.
Поддержка протоколов второго уровня
Еще один большой шаг вперед, сделанный SegWit, заключается в том, что он поддерживает разработку протоколов второго уровня. Сегвит сделал любую функцию, которая основывалась на неподтвержденных транзакциях, менее рискованной и удобной в проектировании.
Активация SegWit также способствовала развитию работы над другими функциями, такими как MAST (что позволяет создавать более сложные Биткоин-смарт-контракты), сигнатуры Schnorr (что позволит повысить производительность транзакций) и TumbleBit (анонимная сеть верхнего уровня).
Не все счастливы
Далеко не все в сообществе Bitcoin уверены, что SegWit – это решение, которое улучшит работу сети. Ведь количество пользователей и транзакций будет расти, и даже блок в 2 МБ в дальнейшем будет маленьким для потребностей Блокчейн системы.
Противники протокола Сегвит считают, что оно оголяет систему, так как, увеличивая размер блока, протокол увеличивает количество неподтвержденных транзакций. А это приведет к уязвимости сети, и возможным хакерским атакам.
Перспективы SegWit
Несмотря на очевидные преимущества, внедрение приложения движется медленно. Только 14% транзакций использовали новый формат.
Основная причина в том, что многие кошельки еще не добавили поддержку SegWit. Некоторые крупные имена, такие как Trezor, Ledger, Electrum и Kraken, уже сделали это. Coinbase – крупнейший поставщик кошельков по количеству транзакций – работает над этим, и ожидается, что он начнет обновление в начале 2018 года. И кошелек, связанный с самой популярной полноразмерной версией Bitcoin, Bitcoin Core, как ожидается, выведет SegWit в первом квартале 2018 года.
Основной код Биткоина, который также делает корректировки, совместимые с SegWit, может привести к повышению производительности, как при использовании, так и при проведении дополнительных экспериментов. Bitcoin Core поддерживает список на своем веб-сайте предприятий и проектов, работающих над интеграцией SegWit – было развернуто 19 реализаций, а еще 90 готовы к работе.
По мере увеличения количества кошельков, связанных с обновлением, процент транзакций, использующих структуру SegWit, будет увеличиваться. А плата Биткоинов должна снижаться, поскольку блоки содержат большее количество транзакций. Кроме того, разработка молнии и аналогичных протоколов второго уровня должна стать более стимулирующей, увеличивая масштабы и потенциал Bitcoin. Это вряд ли произойдет в одночасье, но изменение является важным и представляет собой большой шаг вперед.
Еще больше инсайдов и полезного материала в нашем телеграм канале @CRYPTOSLIVA
Источник
Litecoin (LTC)
1. What is Litecoin (LTC)?
2. Litecoin’s key features
Core concepts of Bitcoin, blockchains, and the Nakamoto consensus are not discussed in this report. Please read our report about Bitcoin (BTC) (section “core features”). For a beginner introduction to Bitcoin and blockchains, please visit Binance Academy’s mega-guide to Bitcoin.
Segregated Witness (shared with Bitcoin)
Segregated Witness (often abbreviated to SegWit) is a protocol upgrade proposal that went live in May 2017 2 for Litecoin (vs. August 2017 for Bitcoin).
It separates witness signatures from transaction-related data. Witness signatures in “legacy Bitcoin blocks” often take more than 50% of the block size. By removing witness signatures from the transaction block, this protocol effectively increases the number of transactions that can be stored in a single block, rendering the network capable of handling more transactions per second. As a result, SegWit increases the scalability of Nakamoto consensus-based blockchain networks Litecoin.
SegWit also makes transactions cheaper. Since transaction fees are derived from how much data is being processed by the block producer, the more transactions that can be stored in a 1MB block, the cheaper individual transactions become.
The legacy Bitcoin block has a block size limit of 1 megabyte, and any change on the block size would require a network hard-fork. On August 1st 2017, the first chain split occurred, leading to the creation of Bitcoin Cash (BCH), which introduced an 8 megabyte limit per block.
Conversely, Segregated Witness was a soft-fork: it never changed the transaction block-size limit of the network. Instead, it has added an extended block with an upper limit of 3 megabytes, which contains solely witness signatures, to the 1-megabyte block that contains only transaction data. This new block type can be processed even by nodes that have not completed this protocol upgrade.
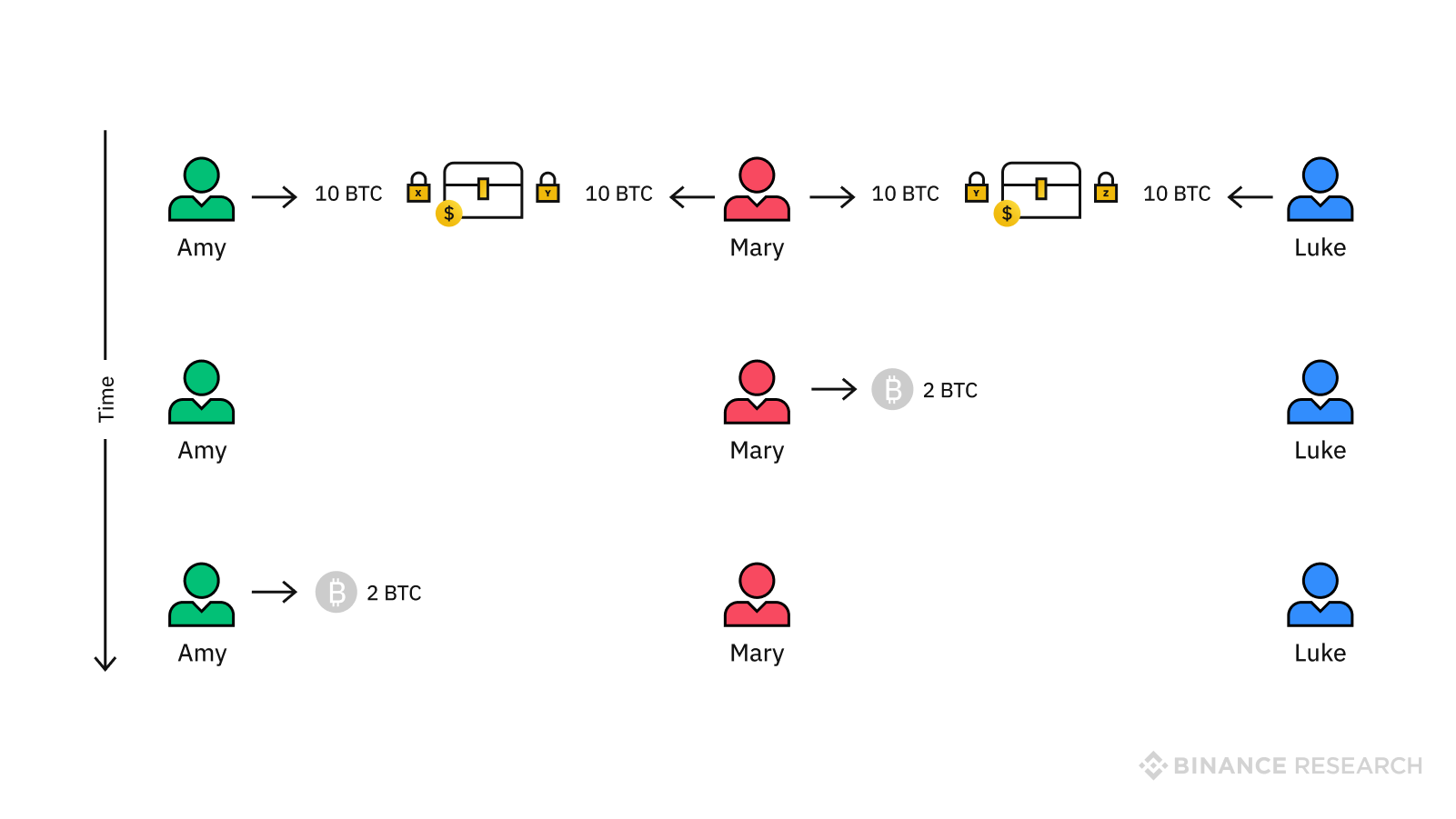
Furthermore, the separation of witness signatures from transaction data solves the malleability issue of blockchains using the Nakamoto consensus. Without Segregated Witness, these signatures could be altered before the block is validated by miners. Indeed, alterations can be done in such a way that if the system does a mathematical check, the signature would still be valid. However, since the values in the signature are changed, the two signatures would create vastly different hash values.
For instance, if a witness signature states “6,” it has a mathematical value of 6, and would create a hash value of 12345. However, if the witness signature were changed to “06”, it would maintain a mathematical value of 6 while creating a (faulty) hash value of 67890.
Since the mathematical values are the same, the altered signature remains a valid signature. Hence, this would create a bookkeeping issue, as transactions in Nakamoto consensus-based blockchain networks are documented with these hash values or transaction IDs. Effectively, one can alter a transaction ID to a new one, and the new ID can still be valid.
This can create many issues as illustrated below:
- Alice sends Bob 1 BTC, and Bob sends Merchant Carol this 1 BTC for some goods.
- Bob sends Carols this 1 BTC, while the transaction from Alice to Bob is not yet validated. Carol sees this incoming transaction of 1 BTC to him, and immediately ships goods to B.
- At the moment, the transaction from Alice to Bob is still not confirmed by the network, and Bob can change the witness signature, therefore changing this transaction ID from 12345 to 67890.
- Now Carol will not receive his 1 BTC, as the network looks for transaction 12345 to ensure that Bob’s wallet balance is valid.
- As this particular transaction ID changed from 12345 to 67890 the network will not be able to find this. The transaction from Bob to Carol will fail, and Bob gets his goods while still holding his BTC.
With the Segregated Witness update, such instances can not happen again. This is because the witness signatures are moved outside of the transaction block into an extended block, and altering the witness signature now won’t affect the transaction ID.
Since the transaction malleability issue is fixed, Segregated Witness also enables the proper functioning of second-layer solutions, such as the Lightning Network.
Lightning Network (shared with Bitcoin)
Lightning Network is a micropayment solution based on the Bitcoin protocol. It aims to enable near-instant and low-cost payments between merchants and customers that use Bitcoin.
Specifically, Lightning Network aims to enable near-instant and low-cost payments between merchants and customers that wish to use bitcoins.
Lightning Network was conceptualized in a whitepaper by Joseph Poon and Thaddeus Dryja in 2015. Since then, it has been implemented by multiple companies. The most prominent of them include Blockstream, Lightning Labs, and ACINQ.
For a list of curated resources relevant to Lightning Network, please visit this link.
In the Lightning Network, if a customer wishes to transact with a merchant, both of them need to open a payment channel, which operates off the Bitcoin blockchain (i.e., off-chain vs. on-chain). None of the transaction details from this payment channel are recorded on the blockchain. Hence, only when the channel is closed will the end result of both party’s wallet balances be updated to the blockchain. The blockchain only serves as a settlement layer for Lightning transactions.
Since all transactions done via the payment channel are conducted independently of the Nakamoto consensus, both parties involved in transactions do not need to wait for network confirmation on transactions. Instead, transacting parties would pay transaction fees to Bitcoin miners only when they decide to close the channel.
One limitation to the Lightning Network is that it requires a person to be online in order for him to receive transactions attributing towards him. Another limitation in user experience could be that one needs to lock up some funds every time he wishes to open a payment channel, and is only able to use that fund within the channel.
However, this does not mean he needs to create new channels every time he wishes to transact with a different person on the Lightning Network. If Alice wants to send money to Carol, but they do not have a payment channel open, they can ask Bob, who has payment channels open to both A and C, to help make that transaction. Alice will be able to send funds to Bob, and Bob to Carol. Hence, the number of “payment hubs” (i.e., Bob in the previous example) correlates with both the convenience and the usability of the Lightning Network for real-world applications.
MimbleWimble as a privacy feature (in implementation)
MimbleWimble is a data storage and transaction structure that aims to enhance privacy and fungibility while reducing network bloating and improving scalability. The Mimblewimble design was introduced in 2016 by pseudonymous Tom Elvis Jedusor. As of April 2020, MimbleWimble’s main stand-alone implementations are Grin (GRIN) and Beam (BEAM).
MimbleWimble is based on the UTXO model. However, in MimbleWimble there are no addresses, and UTXO values are encrypted by the «blinding factors». Blinding factors are private keys which are only known to the UTXO owner. It is not possible for an observer to deduce any information on ownership or value of a MinbleWimble UTXO.
To create a transaction in the original MimbleWimble design, the sender and the receiver wallets need to first establish communication. Once the communication is established, the sender provides the transaction inputs, and both sender and receiver create their respective outputs with range proofs attesting that the values are non-negative. Both parties sign the transaction before sending out to the nodes.
Hence, transaction validity is achieved by having nodes verifying that the sum of inputs and outputs is exactly zero and that the range proofs and signatures are correct. Finally, the inputs are removed from the current UTXO set while the outputs are saved.
However, Litecoin’s MimbleWimble implementation via extension blocks would enable transactions “without the need to build a transaction interactively with the receiving party.” Specifically, Litecoin aims to achieve a similar result with Diffie-Hellman Key Exchange.
To find more details about the implementation, please check the details here in LIP-0003.
3. Economics and supply distribution
Litecoin utilizes the Nakamoto consensus, and nodes validate blocks via Proof-of-Work mining.
Litecoin was not pre-mined, and has a maximum supply of 84 million, exactly 4 times that of Bitcoin. The initial reward for a block is 50 litecoins, and halves every 840,000 blocks. Since the target time for block production on the Litecoin blockchain is 2.5 minutes, it implies that Litecoin block reward halving will take place every 4 years.
4. Project team
Litecoin’s development was initiated by Charlie Lee, and has been maintained by core developers and contributors from the community.
All development activities can be found here.
In addition, the Litecoin Foundation is actively involved in the development and the promotion of Litecoin use-cases across the globe.
The table below shows some of the most prominent members from the Litecoin Foundation.
Источник