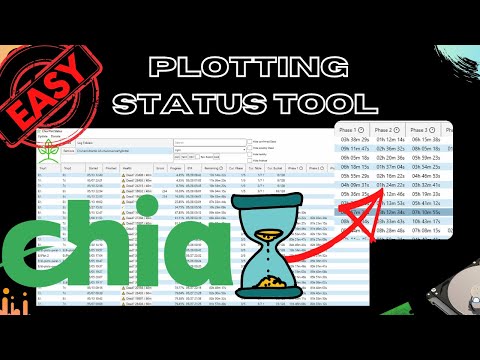
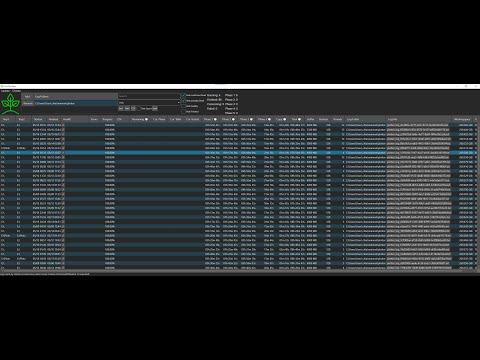
- Chia-Plot-Status
- GUI Tool for beginners and experts to Monitor and Analyse Chia Plotting log files, show health and progress of running plots and estimated time to completion. No setup, configuration or installation of python or whatever required. Just install and enjoy.
- Features
- See Chia Plot Status in action:
- On Upside Down Crypto (YouTube):
- On Patro TV (YouTube):
- How it works
- Working with many distributed plotting rigs
- Security / Trustworthiness
- There are multiple attack vectors to consider:
- 2. The core developer (me) merges a pull request (code changes made by someone else) which contains malicious code without noticing
- 3. External Dependencies (as in libraries / code written by someone else) the application uses to do certain things (like to create the graphical user interface) become malicious.
- Installation / Download
- Getting Log Files from PowerShell
- How to check chia logs
- How to check chia logs
- Launching GitHub Desktop
- Launching GitHub Desktop
- Launching Xcode
- Launching Visual Studio Code
- Latest commit
- Git stats
- Files
- README.md
Chia-Plot-Status
GUI Tool for beginners and experts to Monitor and Analyse Chia Plotting log files, show health and progress of running plots and estimated time to completion. No setup, configuration or installation of python or whatever required. Just install and enjoy.

Features
- Monitor Progress of running plots
- Show estimated time to completion based on your already finished plots best matching your current plot config
- Monitor Health of plotting processes
- Already compatible with madMAx43v3r/chia-plotter (currently getting improved)
- Compatible with all plotters and plotting managers that use or are based on the official chia plotter (see Troubleshooting if something does not work from the get go)
- Show important information from log file in easy to read table
- Multiple folders with log files supported (multiple plotting rigs, anyone?)
- Multiple plots per log file supported (plot create –num n)
- Export of readable or raw data to Json, Yaml and CSV
See Chia Plot Status in action:
On Upside Down Crypto (YouTube):
On Patro TV (YouTube):
How it works
Chia Plot Status observes the log folders you give it to monitor which can be local or connected via network. By this it supports monitoring multiple plotting rigs as you can access them on your desktop even if your plotting rigs are headless. It regulary checks for new Log files in those folders and analyses them.
On basis of finished plots it builds a local statistic (on your machine, no data is send anywhere or pulled from any cloud) and uses them to calculate ETA / time remaining and warning thresholds for the Health of your plotting processes.
Working with many distributed plotting rigs
Recommended way: Use sshfs (with sshfs-win for Windows) to securely mount the log dirs of your plotting rigs on your desktop via highly encrypted network connection, where it is your desktop that initiates the mount. This can be set up so that the desktop can only access the log dirs and only has read access. Even if you use remote plotting rigs that you access over the internet this is the most secure way and you most likely access your remote servers via ssh already.
Other Options: Mount the log folders of all rigs as network shares (via samba on linux) if all your plotting rigs are in the local network or connected via VPN. Another way would be to make a cronjob on your plotting rigs that uses scp or rsync in append mode to copy the log dir to your desktop where you run Chia Plot Status, but if you can manage to set this up you should set up sshfs instead. Last, least preferred option: collect them with cloud apps like Google Drive (Chia Plot Status does not talk to any cloud services for you, you have to install those apps and mount your log folders in them yourself if you want to use them).
Best Practice:
- Only delete log files of finished plots if your hardware or the way you plot has significantly changed. Chia Plot Status uses finished plots to calculate ETA/Time Remaining as well as warning/error thresholds. If you delete finished log files the quality of those values decreases significantly.
- Use SSHFS to access the log directories of your plotting rigs
- Each plotting rig should have its own log folder, so they don’t mix and mess up estimates and warning thresholds for each other.
- Always log locally. If you log directly to a network share / NAS your plotting processes will crash if the connection becomes flaky. Prefer connecting your host machine (which runs Chia Plot Status) to networkshares on the plotting rigs, not the other way around.
Security / Trustworthiness
There are multiple attack vectors to consider:
1. The possibility that the core developer (me) is or becomes malicious
There is a saying: Where is a money trail, there is a way to sue/prosecute someone.
Chia Plot Status has buttons to donate via paypal both in the application itself and on the website.
Should the core developer (me) turn malicious, people could easily sue the core developer (me) and by that get the necessary details as in full name, address and day of birth, IBAN/Bic, everything from paypal.
If the core developer (me) becomes malicious this would be basically a how to get imprisoned speedrun (any %)
Even if you think you would not sue the core developer as he (me) might sit in a different country (germany), someone will as the Chia Plot Status Github Repository has between 2k to 4k visits daily and currently 24k downloads.
This should be more than enough to deter the core developer (me) from doing anything malicious.
2. The core developer (me) merges a pull request (code changes made by someone else) which contains malicious code without noticing
As seen on https://github.com/grayfallstown/Chia-Plot-Status/graphs/contributors there is only one other person who contributed a pull request so far and that wasn’t code but a documentation change.
The core developer (me) will check each pull request before merging as he (me) would have to run the code himself to check if the application works properly after merging that pull request and by that he (I) would get attacked by any malicious code that was contained in that pull request.
3. External Dependencies (as in libraries / code written by someone else) the application uses to do certain things (like to create the graphical user interface) become malicious.
Well, this is a tough one as even the core developer (me) has very little means to check external binaries for malicious code. The core developer (me) and every other developer using those libraries will get attacked by any malicious code in those libraries before they (we) distribute a new version of their (our) software containing that library to the users of their (our) softwares, as they (we) generally test their (our) applications before each release.
The core developer (me) takes the following precautions to mitigate that risk:
External dependencies are kept at a minimum to reduce this attack vector (chia-blockchain devs do the same)
Every release build is build on the same system and previously downloaded dependencies are never deleted/redownloaded. This prevents pulling in malicious code if the external dependency version used gets replaced with malicious code. But it also prevents reproducible builds that everyone can follow and reproduce step by step on their system, if the external dependency version actually does get changed. Well, this should raise concern anyway and in any case.
Updating Dependencies (external libraries / code written by someone else) is delayed (possibly indefinitely) until an update is required to implement a feature or to fix a bug. This gives anti virus providers time to determine if that library version is malicious, which would prevent an update.
Installation / Download
Windows: Download latest version You will get a blue warning saying this was published by an unknown developer.
Linux: First install dotnet 5.0 SDK, then either the Chia Plot Status deb or rpm package depending on your linux distribution (deb for ubuntu)
For Mac you currently have to build it.
Getting Log Files from PowerShell
The last part with 2>&1 | % ToString | Tee-Object writes the log to the PowerShell and to a file with a unique name for each plotting process.
Источник
How to check chia logs
Installing Chiadog on Windows
This is still considered experimental. If you have any issues please report them after browsing the existing issues labeled with bug to avoid duplicates.
If you get unexpected «Your harvester appears offline! No events for the past xxxx seconds» notifications, please report here.
- Windows / Windows + WSL(Ubuntu)
- Python 3.7+
- Git
- Enabled INFO logs on your chia farmer
This guide contains instructions on how to set up a local chiadog consumer on Windows. If you are looking for instructions on how to set up remote monitoring on a Windows machine, please refer to this article instead.
Looking for installation instructions for Linux or MacOS? Head over to the general README.
How to enable INFO logs on chia farmer?
First we’ll set Chia’s log level to INFO . This ensures that all logs necessary for chiadog to operate are available under C:\Users\[YOUR-USER]\.chia\mainnet\log\debug.log .
- Open the file C:\Users\[YOUR-USER]\.chia\mainnet\config\config.yaml in your favorite text editor
- Find the line that reads log_level: DEBUG (under the farmer section) and change this to log_level: INFO
- Restart the GUI or run chia start —restart farmer from the command line
1.1 Powershell(Native) Installation
For updating from previous version, see section below.
Open a PowerShell command line
Clone the repository somewhere on your computer (ex. C:\Users\[YOUR-USER]\ )
- Create a virtual environment for chiadog to run in
Note: if you get an error saying ‘The term ‘python.exe’ is not recognized’ or ‘Python was not found’, change python.exe in the last line of the above code block to py.exe or python3.exe . If none of these work, it is likely that Python was not installed on your system. Refer to this website in order to download the latest version.
- Update pip package manager and install chiadog dependencies
- Make a copy of the example config file
- Open up the newly created config.yaml in your favorite text editor and configure it to your preferences.
1.2 WSL(Ubuntu) Installation
Reminder: INFO level log in Chia must be enabled ( chia configure -log-level=INFO )
Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL): Allows you to run Linux distributions (e.g. Ubuntu) within Windows 10. If you don’t have WSL already, follow the instructions here.
Open up config.yaml in your editor
4.1 Set chia log location:
4.2 configure it to your preferences for notification services (same as OSX/Ubuntu)
Updating to the latest release
Skip this if you just did a fresh install of chiadog .
Important: Automated migration of config is not supported. Please check that your config.yaml has all new fields introduced in config-example.yaml and add anything missing. If correctly migrated, you shouldn’t get any ERROR logs.
Monitoring a local harvester / farmer
Open config.yaml and configure file_log_consumer :
- You need to enable the file log consumer to read local chia log files
- Double-check that the path to your chia logs is correct
- The file path to the log file on Windows needs to be specified in full. E.g. C:\Users\[YOUR-USER]\.chia\mainnet\log\debug.log
Launch the watchdog:
Note: You may also create a shortcut to this script and move it to any convenient name and location to launch chiadog by double-clicking it.
- Verify that your plots are detected. Within a few seconds you should see INFO log:
Monitoring a remote harvester
Chiadog allows you to monitor multiple remote harvesters while running chiadog on a separate machine. Please refer to the Wiki article on Monitoring Remote Harvesters for more information on how to set this up.
Источник
How to check chia logs
Bash script that post-processes chia plotter’s logs to see your statistics
Use Git or checkout with SVN using the web URL.
Work fast with our official CLI. Learn more.
Launching GitHub Desktop
If nothing happens, download GitHub Desktop and try again.
Launching GitHub Desktop
If nothing happens, download GitHub Desktop and try again.
Launching Xcode
If nothing happens, download Xcode and try again.
Launching Visual Studio Code
Your codespace will open once ready.
There was a problem preparing your codespace, please try again.
Latest commit
Git stats
Files
Failed to load latest commit information.
README.md
Chia log analyzer | Анализатор логов Chia
Bash script that post-processes chia plotter’s logs to see your statistics
Баш-скрипт, обрабатывающий логи плоттера Чиа, для получения полезной статистики. Русское ридми — ниже
Have you ever considered what’s your best plotting options? Forget to write down some values during plotting? That’s no longer a problem due to this script.
- Linux
- Bash and standard CLI tools installed [awk, grep] (most of Linux distros has this installed)
- Existing log files from chia plotting
What is inside this repo
- chiacheck_all.sh — Script that builds statistics from all files, both from finished and cancelled plots.
- chiacheck_onlyfinished.sh — Script that builds statistics from only finished plots.
- README.md — this file (the one that you’re reading now)
- LICENSE — Copy of MIT license file.
- Two images illustrating program outputs.
Note: no demo files are provided. The script won’t work as-is unless copied to Chia Plotter Log directory.
This script (without modifications) should reside in plotter’s log directory, which by default can be found here:
/.chia/mainnet/plotter/ . If your path differs from this, please change the commands accordingly.
- Enter your plotting directory: cd
/.chia/mainnet/plotter/
NB! If the script does not run, please, mark .sh files for execution: chmod +x *sh
P.S. Theoretically, this script can use Mac/Win logs as well, but you will need to use Linux to run it anyways. You can do it from live USB flash or virtual machine, if you want to.
Further improvements & questions
Feel free to send your ideas, questions and bug reports into the «issues» of this project. Also, if you’ll manage to add some cool functionality, please send me a pull request.
You can support me directly via Github (Sponsors), or on my webpage https://sxiii.ru/donate
Задумывались ли вы когда-то, оптимальные ли настройки плоттинга у вас заданы? Забывали записывать ваши тестовые параметры? Это больше не проблема, благодаря данному скрипту.
- Linux
- Bash и стандартные CLI инструменты [awk, grep] (большинство Linux-дистрибутивов уже имеет их)
- Лог-файлы плоттинга Чиа (они у вас уже должны быть)
Что в этом репозитории
- chiacheck_all.sh — Скрипт, собирающий статистику из всех ваших файлов (включая отменённые/незавершённые плоты)
- chiacheck_onlyfinished.sh — Скрипт, собирающий статистику только о успешно «нарисованных» плотах.
- README.md — этот файл (что вы сейчас читаете)
- LICENSE — Копия лицензии MIT.
- Два изображения с иллюстрациями данных, которые может выводить программа.
Внимание: демо-файлы не предоставляются. Скрипт не будет работать в текущем виде, если вы не поместите его в директорию с логами плоттинга Chia.
Этот скрипт (без модификаций) необходимо расположить в папку с логами плоттера, которая в Linux по умолчанию находится вот тут:
/.chia/mainnet/plotter/ . Если ваш путь с логами плоттера отличается, пожалуйста, исправьте следующие команды в соответствии с ним.
- Входим в папку с логами плоттера: cd
/.chia/mainnet/plotter/
NB! Если скрипт не запускается на шаге 3, пожалуйста, сделайте SH файлы исполняемыми: chmod +x *sh
P.S. Теоритически, этот скрипт может работать так же с логами с платформ Mac/Win, но вам всё равно понадобится Linux чтобы запустить его. Вы, разумеется, можете запустить Linux для этого с живой флэшки или в виртуальной машине, если у вас нет полноценной установки.
Предложения, вопросы и баг-репорты пишите в Issues данного проекта. Так же, если добавите какой-то классный функционал, присылайте pull-request.
Источник