Nodes and clients
Ethereum is a distributed network of computers running software (known as nodes) that can verify blocks and transaction data. You need an application, known as a client, on your computer to «run» a node.
You should understand the concept of a peer-to-peer network and the basics of the EVM before diving deeper and running your own instance of an Ethereum client. Take a look at our introduction to Ethereum.
What are nodes and clients?
«Node» refers to a running piece of client software. A client is an implementation of Ethereum that verifies all transactions in each block, keeping the network secure and the data accurate.
You can see a real-time view of the Ethereum network by looking at this map of nodes.
Many Ethereum clients exist, in a variety of programming languages such as Go, Rust, JavaScript, Python, C# .NET and Java. What these implementations have in common is they all follow a formal specification (originally the Ethereum Yellow Paper). This specification dictates how the Ethereum network and blockchain functions.

If you want to run your own node, you should understand that there are different types of node that consume data differently. In fact, clients can run 3 different types of node — light, full and archive. There are also options of different sync strategies which enables faster synchronization time. Synchronization refers to how quickly it can get the most up-to-date information on Ethereum’s state.
- Stores full blockchain data.
- Participates in block validation, verifies all blocks and states.
- All states can be derived from a full node.
- Serves the network and provides data on request.
- Stores the header chain and requests everything else.
- Can verify the validity of the data against the state roots in the block headers.
- Useful for low capacity devices, such as embedded devices or mobile phones, which can’t afford to store gigabytes of blockchain data.
- Stores everything kept in the full node and builds an archive of historical states. Needed if you want to query something like an account balance at block #4,000,000.
- These data represent units of terabytes which makes archive nodes less attractive for average users but can be handy for services like block explorers, wallet vendors, and chain analytics.
Syncing clients in any mode other than archive will result in pruned blockchain data. This means, there is no archive of all historical state but the full node is able to build them on demand.
Why should I run an Ethereum node?
Running a node allows you to trustlessly and privately use Ethereum while supporting the ecosystem.
Benefits to you
Running your own node enables you to use Ethereum in a truly private, self-sufficient and trustless manner. You don’t need to trust the network because you can verify the data yourself with your client. «Don’t trust, verify» is a popular blockchain mantra.
- Your node verifies all the transactions and blocks against consensus rules by itself. This means you don’t have to rely on any other nodes in the network or fully trust them.
- You won’t have to leak your addresses and balances to random nodes. Everything can be checked with your own client.
- Your dapp can be more secure and private if you use your own node. Metamask, MyEtherWallet and some other wallets can be easily pointed to your own local node.

A diverse set of nodes is important for Ethereum’s health, security and operational resiliency.
- They provide access to blockchain data for lightweight clients that depend on it. In high peaks of usage, there need to be enough full nodes to help light nodes sync. Light nodes don’t store the whole blockchain, instead they verify data via the state roots in block headers. They can request more information from blocks if they need it.
- Full nodes enforce the proof-of-work consensus rules so they can’t be tricked into accepting blocks that don’t follow them. This provides extra security in the network because if all the nodes were light nodes, which don’t do full verification, miners could attack the network and, for example, create blocks with higher rewards.
If you run a full node, the whole Ethereum network benefits from it.
Running your own node
Interested in running your own Ethereum client? Learn how to spin up your own node!
ethnode — Run an Ethereum node (Geth or Parity) for local development.
DAppNode — An operating system GUI for running Web3 nodes, including Ethereum and the beacon chain, on a dedicated machine.
- Running Ethereum Full Nodes: A Complete GuideNov 7, 2019 — Justin Leroux
- Node Configuration Cheat SheetJan 5, 2019 — Afri Schoeden
- How To Install & Run a Geth NodeOct 4, 2020 — Sahil Sen
- How To Install & Run a OpenEthereum (fka. Parity) NodeSept 22, 2020 — Sahil Sen
Running your own node can be difficult and you don’t always need to run your own instance. In this case, you can use a third party API provider like Infura, Alchemy, or QuikNode. Alternatively ArchiveNode is a community-funded Archive node that hopes to bring archive data on the Ethereum blockchain to independent developers who otherwise couldn’t afford it. For an overview of using these services, check out nodes as a services.
If somebody runs an Ethereum node with a public API in your community, you can point your light wallets (like MetaMask) to a community node via Custom RPC and gain more privacy than with some random trusted third party.
On the other hand, if you run a client, you can share it with your friends who might need it.
The Ethereum community maintains multiple open-source clients, developed by different teams using different programming languages. This makes the network stronger and more diverse. The ideal goal is to achieve diversity without any client dominating to reduce any single points of failure.
This table summarises the different clients. All of them are actively worked on and pass client tests.
| Client | Language | Operating systems | Networks | Sync strategies | State pruning |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Geth | Go | Linux, Windows, macOS | Mainnet, Görli, Rinkeby, Ropsten | Fast, Full, Snap | Archive, Pruned |
| OpenEthereum | Rust | Linux, Windows, macOS | Mainnet, Kovan, Ropsten, and more | Warp, Full | Archive, Pruned |
| Nethermind | C#, .NET | Linux, Windows, macOS | Mainnet, Görli, Ropsten, Rinkeby, and more | Fast, Full | Archive, Pruned |
| Besu | Java | Linux, Windows, macOS | Mainnet, Rinkeby, Ropsten, and Görli | Fast, Full | Archive, Pruned |
| Trinity | Python | Linux, macOS | Mainnet, Görli, Ropsten, and more | Full, Beam, Fast/Header | Archive |
| Erigon | Go / Multi | Linux, Windows, macOS | Mainnet, Görli, Rinkeby, Ropsten | Full | Archive, Pruned |
For more on supported networks, read up on Ethereum networks.
Advantages of different implementations
Each client has unique use cases and advantages, so you should choose one based on your own preferences. Diversity allows implementations to be focused on different features and user audiences. You may want to choose a client based on features, support, programming language, or licences.
Go Ethereum (Geth for short) is one of the original implementations of the Ethereum protocol. Currently, it is the most widespread client with the biggest user base and variety of tooling for users and developers. It is written in Go, fully open source and licensed under the GNU LGPL v3.
OpenEthereum is a fast, feature-rich and advanced CLI-based Ethereum client. It’s built to provide the essential infrastructure for speedy and reliable services which require fast synchronisation and maximum up-time. OpenEthereum’s goal is to be the fastest, lightest, and most secure Ethereum client. It provides a clean, modular codebase for:
- easy customisation.
- light integration into services or products.
- minimal memory and storage footprint.
OpenEthereum is developed using the cutting-edge Rust programming language and licensed under the GPLv3.
Nethermind is an Ethereum implementation created with the C# .NET tech stack, running on all major platforms including ARM. It offers great performance with:
- an optimized virtual machine
- state access
- networking and rich features like Prometheus/Graphana dashboards, seq enterprise logging support, JSON RPC tracing, and analytics plugins.
Nethermind also has detailed documentation, strong dev support, an online community and 24/7 support available for premium users.
Hyperledger Besu is an enterprise-grade Ethereum client for public and permissioned networks. It runs all of the Ethereum mainnet features, from tracing to GraphQL, has extensive monitoring and is supported by ConsenSys, both in open community channels and through commercial SLAs for enterprises. It is written in Java and is Apache 2.0 licensed.
Erigon is a completely re-architected implementation of Ethereum, currently written in Go but with implementations in other languages planned. Erigon’s goal is to provide a faster, more modular, and more optimized implementation of Ethereum. It can perform a full archive node sync using less than 2TB of disk space, in under 3 days.
- Full – downloads all blocks (including headers, transactions and receipts) and generates the state of the blockchain incrementally by executing every block.
- Fast (Default) – downloads all blocks (including headers, transactions and receipts), verifies all headers, and downloads the state and verifies it against the headers.
- Light – downloads all block headers, block data, and verifies some randomly.
- Warp sync – Every 5,000 blocks, nodes will take a consensus-critical snapshot of that block’s state. Any node can fetch these snapshots over the network, enabling a fast sync. More on Warp
- Beam sync – A sync mode that allows you to get going faster. It doesn’t require long waits to sync, instead it back-fills data over time. More on Beam
- Header sync – you can use a trusted checkpoint to start syncing from a more recent header and then leave it up to a background process to fill the gaps eventually
You define the type of sync when you get set up, like so:
Setting up light sync in GETH
geth —syncmode «light»
Setting up header sync in Trinity
trinity —sync-from-checkpoint eth://block/byhash/0xa65877df954e1ff2012473efee8287252eee956c0d395a5791f1103a950a1e21?score=15,835,269,727,022,672,760,774
Hardware requirements differ by client but generally are not that high since the node just needs to stay synced. Don’t confuse it with mining which requires much more computing power. Sync time and performance do improve with more powerful hardware however. Depending on your needs and wants, Ethereum can be run on your computer, home server, single-board computers or virtual private servers in the cloud.
An easy way to run your own node is using ‘plug and play’ boxes like DAppNode. It provides hardware for running clients and applications that depend on them with a simple user interface.
Before installing any client, please ensure your computer has enough resources to run it. Minimum and recommended requirements can be found below, however the key part is the disk space. Syncing the Ethereum blockchain is very input/output intensive. It is best to have a solid-state drive (SSD). To run an Ethereum client on HDD, you will need at least 8GB of RAM to use as a cache.
- CPU with 2+ cores
- 4 GB RAM minimum with an SSD, 8 GB+ if you have an HDD
- 8 MBit/s bandwidth
- Fast CPU with 4+ cores
- 16 GB+ RAM
- Fast SSD with at least 500 GB free space
- 25+ MBit/s bandwidth
Depending on which software and sync mode are you going to use, hundreds of GBs of disk space is need. Approximate numbers and growth can be found below.
| Client | Disk size (fast sync) | Disk size (full archive) |
|---|---|---|
| Geth | 400GB+ | 6TB+ |
| OpenEthereum | 280GB+ | 6TB+ |
| Nethermind | 200GB+ | 5TB+ |
| Besu | 750GB+ | 5TB+ |
| Erigon | N/A | 1TB+ |
- Note: Erigon does not Fast Sync, but Full Pruning is possible (


These charts show how storage requirements are always changing. For the most up-to-date data for Geth and OpenEthereum, see the full sync data and archive sync data.
Ethereum on a single-board computer
The most convenient and cheap way of running Ethereum node is to use a single board computer with ARM architecture like Raspberry Pi. Ethereum on ARM provides images of Geth, Parity, Nethermind, and Besu clients. Here’s a simple tutorial on how to build and setup an ARM client.
Small, affordable and efficient devices like these are ideal for running a node at home.
There are new clients to support the Eth2 upgrades. They will run the Beacon Chain and support the new proof-of-stake consensus mechanism.
There is a lot of instructions and information about Ethereum clients on the internet, here are few that might be helpful.
Источник
Установка и настройка ноды для Ethereum
Выполняя проекты на блокчейне мы столкнулись с тем, что в интернете нет информативной статьи, которая подробно рассказывала бы, как развернуть ноду и выполнить простейшие команды.
Что такое нода?
Нода — это любой компьютер, подключенный к блокчейн-сети. Через P2P-протоколы ноды обмениваются между собой информацией о блоках и транзакциях.
В зависимости от типа ноды хранят только часть или все данные блокчейна и делятся на:
- Полные ноды. Они обслуживают всю сеть, загружают и валидируют каждый блок с транзакциями, руководствуясь исключительно алгоритмом консенсуса, и являются полностью независимыми. Полные ноды отвергают противоречащие консенсусу блоки или отдельные транзакции. Такая нода имеет полную копию данных сети блокчейна.
- Облегченные ноды. Представляют компьютер со специальным ПО, подключенный к сети блокчейн. Облегченные ноды не хранят все данные блокчейна, а только заголовки блоков для подтверждения подлинности транзакций, которые они содержат.
Системные требования для работы ноды криптовалюты Ethereum
Для полноценной работы с приложениями необходимо “поднимать” полную ноду. Самый важный и проблемный вопрос — наличие подходящего железа. Бюджетные виртуальные сервера не смогут должным образом поддерживать работу нод, их мощности просто не хватит. А некоторые криптовалюты, такие как Ethereum и Bitcoin, требуют большой объем жесткого диска — около терабайта.
Для работы ноды нужен выделенный сервер среднего сегмента. Сервер низкого сегмента брать не стоит, есть риск, что со временем требования к серверу повысятся, нода разрастется, а мощности не хватит. Слишком дорогой сервер тоже не нужен, только если вы не собираетесь на нем держать несколько нод для разных криптовалют.
Размер жесткого диска
Это один из основных моментов, требующих постоянного контроля. Размер ноды Ethereum постоянно растет на несколько десятков гигабайт в месяц. Покупайте сервер с большим запасом места, чтобы не приходилось останавливать работу для его увеличения.
На момент написания статьи рекомендуем иметь ноду на 1,2 Тб — это уже с небольшим запасом на ближайшие 2-3 месяца.
Производительность дисков
Обязательно нужно обращать внимание на производительность жестких дисков. Нода криптовалюты Ethereum содержит огромное количество мелких и очень мелких файлов, количество которых может достигать миллионов. Для этого лучше использовать SSD-диски, т.к. они более быстрые в сравнении с SATA. Нода Ethereum больше всех других нод нагружает систему, поэтому и железо нужно помощнее.
Процессор и память
Минимальные системные параметры для работы ноды Ethereum: 4 ядра процессора и 8 гигабайт оперативной памяти (ОЗУ). Конечно, нода будет работать и на более низких параметрах, но ее стабильность при этом будет куда ниже.
Если на сервере располагается еще какой-то проект, особенно высокофункциональный и нагруженный, рекомендуем повысить эти показатели в 1,5-2 раза.
Операционная система
Нет какой-то определенной рекомендации для конкретного выбора ОС. Мы используем при реализации проектов Ubuntu. Обычно разработчики нод объявляют поддержку именно этой системы. Под нее всегда есть готовые сборки и скрипты установки. С другой версией линукс придется тратить больше времени.
Установка и настройка ноды эфира (etherium)
Если помимо ноды на сервере у вас стоит проект, то для работы с каждой нодой мы рекомендуем создать отдельного пользователей на сервере. Это обезопасит проект от случайной поломки и позволит разграничить доступ к данным.
1. Авторизуемся на сервере:
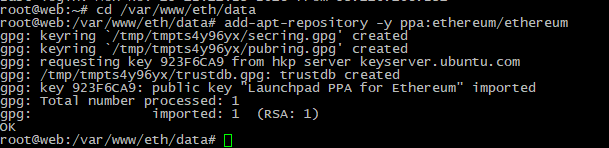
2. Переходим в папку на сервере, где будет располагаться нода. В примере мы создали отдельную папку eth/data/:
3. Добавляем репозиторий ethereum, с которого будут загружены установочные файлы ноды:
# add-apt-repository -y ppa:ethereum/ethereum
4. Обновляем список репозиториев:
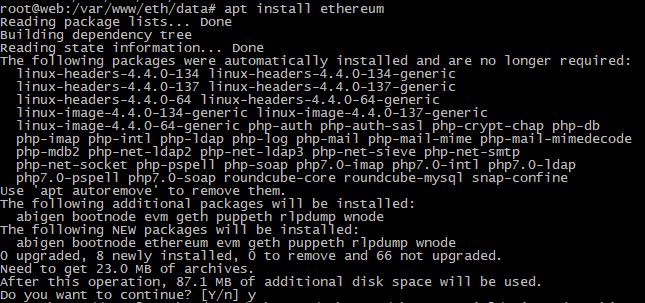
5. Следующей командой запускаем установку ноды Ethereum на сервере:
# apt install ethereum
После запуска команды нас попросят подтвердить операцию, указываем “y” и жмем “Enter”:
В консоли отобразиться длинное полотно лога, это нормально. Ошибок при этом быть не должно:
Нода установлена. Теперь ее нужно запустить.
6. Для запуск ноды выполняем команду:
В консоли начнет отображаться ход запуска ноды и ее синхронизация:
В случае запуска команды без дополнительных параметров нода будет запущена с параметрами по умолчанию. На скриншоте можно видеть что, памяти выделено всего 512 Мб.
7. Чтобы запустить ноду в более быстром режиме, необходимо выполнить команду с параметрами, которые запускают RPC API для возможности обращения к командам API ноды:
# geth —cache=8192 —rpc —rpcaddr 0.0.0.0 —rpcport 8545 —rpccorsdomain «*» —rpcapi «admin,eth,miner,web3,personal»
- cache — размер выделяемой памяти в Мб, рекомендуемое значение 8192, если параметры сервера позволяют;
- rpcaddr — ip-адрес по которому будет работать API ноды, в данном случае это адрес сервера;
- rpcport — порт, через который будет происходить подключение к API ноды:
- rpcapi — для работы достаточно параметров “admin, eth, miner, web3, personal”.
С более подробной информацией о работе с API Ethereum можно ознакомиться на официальной странице в Github https://github.com/ethereum/go-ethereum.
Для быстрого обновления ноды желательно иметь выделенный канал не менее чем 1 Гбит/с. В наших проектах такую скорость связи нам обеспечивает наличие собственного дата-центра.
Поскольку нода может синхронизироваться очень долго, до нескольких дней, есть смысл ее повесить на фоновый процесс вместе с супервизором. Периодически может случаться, что память на сервере заканчивается и ноду необходимо перезапустить. Супервизор будет делать это автоматически, а процесс синхронизации не будет остановлен.
Пока нода запущена — работает API, а вместе с ним и весь функционал по Ethereum.
Команды для работы с нодой на Ethereum
В данном блоке мы перечислили основные команды, которые помогут управлять нодой и обслуживать ее.
Чтобы подключиться к панели управления нодой, необходимо ввести команду:
В консоли отобразится информация о подключении:
В первую очередь нам нужно знать, каков статус синхронизации. Для этого в Панели вводим команду:
Отобразится информация о блоках:
- currentblock — текущий блок в нашей ноде;
- highestblock — значение самого последнего блока в сети.
Наша задача дождаться, пока значение текущего блока будет равно значению последнего. Как только это случилось, консоль нам выдаст статус “false”, означающий, что нода полностью синхронизирована и готова к работе:
Таким образом мы запустили и синхронизировали всю базу Ethereum и готовы к последующей разработке приложения на блокчейн.
Иногда бывает, что нода перестает синхронизироваться из-за битых данных либо вообще не запускается процесс синхронизации, выдает ошибку. В таком случае необходимо очистить базу данных блокчейна командой:
В случае, если после очистки базы нода все-равно медленно синхронизируется или вообще прогресс не идет, нужно проверить наличие подключений пиров. Пиры — это все компьютеры, которые отдают вам свои данные блокчейна, т.е. откуда вы скачиваете базу. Для этого в Панели управления нодой запускаете команду:
Посмотреть, на сколько процентов загружена база от своего общего объема, можно командой, запускать ее нужно в консоли:
# geth —exec ‘var s = eth.syncing; console.log(«\n———— GETH SYNCING PROGRESS\nprogress: » + (s.currentBlock/s.highestBlock*100)+ » %\nblocks left to parse: «+ (s.highestBlock-s.currentBlock) + «\ncurrent Block: » + s.currentBlock + » of » + s.highestBlock)’ attach
Надпись “undefined” означает, что нода синхронизируется в реальном времени, но еще не получила информацию о самом последнем блоке. Это нормально, т.к. ежесекундно появляются новые данные, которые постоянно загружаются в базу блокчейна. Тут скорее следует обращать внимание на общий прогресс синхронизации, чтобы он не сильно отставал, иначе есть риск получения неактуальных данных о блокчейне.
Если вам требуется разработать проект, которые реализован на блокчейн, то вы можете обратиться к нам для расчета стоимости.
Источник