- What is bitcoin?
- Bitcoin is a cryptocurrency created in 2009. Marketplaces called “bitcoin exchanges” allow people to buy or sell bitcoins using different currencies.
- Why bitcoin?
- Buying bitcoins
- Bitcoin wallet
- The anonymity of bitcoin
- Bitcoin’s future in question
- I bought $250 in bitcoin. Here’s what I learned
- Some people kill time at the airport by browsing duty-free shops. I decided to shop for bitcoin.
- What is happening?
- Why would anyone want or need to use bitcoin?
- So is there anything truly valuable about bitcoin?
- Is there a legal and legitimate way to invest in bitcoin?
- What is bitcoin cash? – CNN
- Related articles
- New crypto mining data centres to use 1 GW of Texas renewables
- JPMorgan Issues Stark Bitcoin Warning As Ethereum, Binance’s BNB, Cardano And Dogecoin Slide
- What is the distinction between bitcoin money and bitcoin?
- Prepared to purchase bitcoin money?
- Bitcoin
- Contents
- Basic Concepts [ edit ]
- Currency [ edit ]
- Banks [ edit ]
- Bitcoin Basics [ edit ]
- Buying Bitcoin [ edit ]
- Creation of coins [ edit ]
- Bitcoin Mining [ edit ]
- Sending payments [ edit ]
- Preventing double-spending [ edit ]
- Anonymity [ edit ]
- Capitalization / Nomenclature [ edit ]
- Bitcoin Halving [ edit ]
- Bitcoin price [ edit ]
- Where to see and explore [ edit ]
- How many people use Bitcoin? [ edit ]
- White Paper [ edit ]
What is bitcoin?
Bitcoin is a cryptocurrency created in 2009. Marketplaces called “bitcoin exchanges” allow people to buy or sell bitcoins using different currencies.
Bitcoin is a new currency that was created in 2009 by an unknown person using the alias Satoshi Nakamoto. Transactions are made with no middle men – meaning, no banks! Bitcoin can be used to book hotels on Expedia, shop for furniture on Overstock and buy Xbox games. But much of the hype is about getting rich by trading it. The price of bitcoin skyrocketed into the thousands in 2017.
Why bitcoin?
Bitcoins can be used to buy merchandise anonymously. In addition, international payments are easy and cheap because bitcoins are not tied to any country or subject to regulation. Small businesses may like them because there are no credit card fees. Some people just buy bitcoins as an investment, hoping that they’ll go up in value.
Buying bitcoins
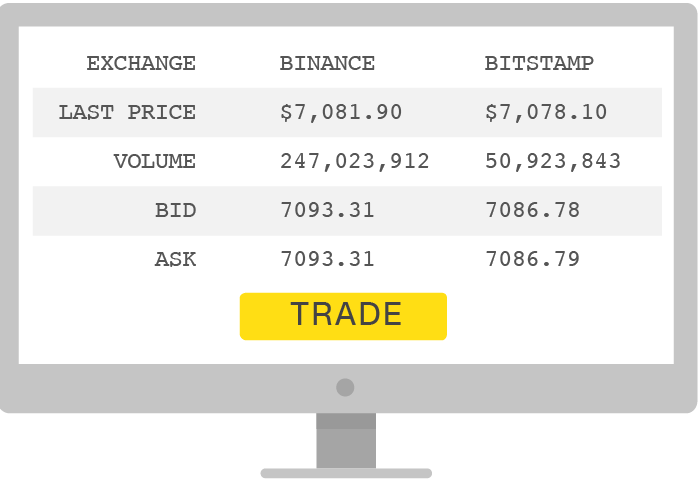
Buy on an Exchange
Many marketplaces called “bitcoin exchanges” allow people to buy or sell bitcoins using different currencies. Coinbase is a leading exchange, along with Bitstamp and Bitfinex. But security can be a concern: bitcoins worth tens of millions of dollars were stolen from Bitfinex when it was hacked in 2016.
People can send bitcoins to each other using mobile apps or their computers. It’s similar to sending cash digitally.
People compete to “mine” bitcoins using computers to solve complex math puzzles. This is how bitcoins are created. Currently, a winner is rewarded with 12.5 bitcoins roughly every 10 minutes.
Bitcoin wallet
Bitcoins are stored in a “digital wallet,” which exists either in the cloud or on a user’s computer. The wallet is a kind of virtual bank account that allows users to send or receive bitcoins, pay for goods or save their money. Unlike bank accounts, bitcoin wallets are not insured by the FDIC.
Wallet in cloud: Servers have been hacked. Companies have fled with clients’ bitcoins.
Wallet on computer: You can accidentally delete them. Viruses could destroy them.
The anonymity of bitcoin
Though each bitcoin transaction is recorded in a public log, names of buyers and sellers are never revealed – only their wallet IDs. While that keeps bitcoin users’ transactions private, it also lets them buy or sell anything without easily tracing it back to them. That’s why it has become the currency of choice for people online buying drugs or other illicit activities.
Bitcoin’s future in question
No one knows what will become of bitcoin. It is mostly unregulated, but some countries like Japan, China and Australia have begun weighing regulations. Governments are concerned about taxation and their lack of control over the currency.
Most stock quote data provided by BATS. Market indices are shown in real time, except for the DJIA, which is delayed by two minutes. All times are ET. Disclaimer. Morningstar: © 2018 Morningstar, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Factset: FactSet Research Systems Inc. 2018. All rights reserved. Chicago Mercantile Association: Certain market data is the property of Chicago Mercantile Exchange Inc. and its licensors. All rights reserved. Dow Jones: The Dow Jones branded indices are proprietary to and are calculated, distributed and marketed by DJI Opco, a subsidiary of S&P Dow Jones Indices LLC and have been licensed for use to S&P Opco, LLC and CNN. Standard & Poor’s and S&P are registered trademarks of Standard & Poor’s Financial Services LLC and Dow Jones is a registered trademark of Dow Jones Trademark Holdings LLC. All content of the Dow Jones branded indices © S&P Dow Jones Indices LLC 2018 and/or its affiliates.
Источник
I bought $250 in bitcoin. Here’s what I learned
Some people kill time at the airport by browsing duty-free shops. I decided to shop for bitcoin.
But first, there are two things you should know about me: I tend to be almost as afraid of losing money investing as I am of flying. On some level, I figured one fear might cancel out the other.
So last Thursday, while waiting for a flight to Nashville, I pulled up a popular application called Coinbase that can be used to buy and sell bitcoin. The virtual currency had hit $10,000 for the first time a couple days earlier, before retreating somewhat. News of bitcoin’s rapid rise was everywhere, including on CNN.
For 15 minutes at the airport, I refreshed the price of bitcoin over and over, watching as it gained and lost hundreds of dollars in a matter of minutes. I called out the price fluctuations breathlessly to my wife, who gently encouraged me not to be an idiot, before returning to her magazine.
She was in good company. JPMorgan Chase CEO Jamie Dimon recently called bitcoin a «fraud» and suggested people who buy it are «stupid.» Warren Buffett called bitcoin a «mirage» in 2014 and warned investors to «stay away.»
Are you trading Bitcoin? We want to hear from you.
And yet bitcoin has climbed more than tenfold since Buffett’s warning. Earlier this month, one college friend casually told me over drinks he’d made tens of thousands of dollars investing in another cryptocurrency. He said he hoped it would be worth enough one day to buy a house.
When I saw the price of bitcoin fall to $9,500, I pressed buy, defying the wisdom of two finance titans and my wife. One hundred dollars, or 0.0101 bitcoins. (A few days later, I bought another $150.) By the time we got to our hotel, my stake had already gone up 10%. One week later, it was (briefly) up 100%. My wife’s opinion of me has reportedly decreased by the same amount.
What is happening?
It’s an investing frenzy, plain and simple.
Bitcoin cracked $1,000 on the first day of 2017. By this week, it was up to $12,000, and then it really took off: The price topped $17,000 on some exchanges Thursday, and $18,000 on at least one. Other cryptocurrencies have seen similar spikes, though they trade for much less than bitcoin.
There’s a long list of factors people may point to in an attempt to explain this. Regulators have taken a hands-off approach to bitcoin in certain markets. Dozens of new hedge funds have launched this year to trade cryptocurrencies like bitcoin. The Nasdaq and Chicago Mercantile Exchange plan to let investors trade bitcoin futures, which may attract more professional investors.
Yet a key reason the price of bitcoin keeps going up is, well, because it keeps going up. Small investors like yours truly have a fear of missing out on a chance to get rich quick. And when the value of your bitcoin doubles in a week, as it did for me, it’s easy to think you’re a genius. But you can get burned assuming it will keep skyrocketing.
Some investors have likened the bitcoin hype to the dot-com bubble. Others, like Dimon, have said it’s even «worse» than the Dutch tulip mania from the 1600s, considered one of the most famous bubbles ever.
As Buffett put it back in 2014, «the idea that [bitcoin] has some huge intrinsic value is just a joke in my view.» Bitcoin is not backed by a company’s earnings, or the strength of a government and rule of law. There’s also no interest or dividends.
Why would anyone want or need to use bitcoin?
Bitcoin serves as a new kind of currency for the digital era. It works across international borders and doesn’t need to be backed by banks or governments.
Or at least that was the promise when it was created in 2009. The surge and volatility of bitcoin this year may be great for those who invested early, but it undermines bitcoin’s viability as a currency.
Right now, I can use my bitcoin holdings to pay for purchases at Overstock ( OSTBP ) , or book a hotel on Expedia ( EXPE ) . But if I use bitcoin to buy $25 worth of socks on Overstock today, and the price of bitcoin quadruples next week, I’ll feel like those socks actually cost me $100. Then again, if bitcoin crashes, at least I’ll always have the socks.
Rather than a currency, bitcoin is being treated more like an asset, with the hope of reaping great returns in the future.
So is there anything truly valuable about bitcoin?
Yes, the technology behind it.
Bitcoin is built on the blockchain, a public ledger containing all the transaction data from anyone who uses bitcoin. Transactions are added to «blocks» or the links of code that make up the chain, and each transaction must be recorded on a block.
Even bitcoin critics like Dimon have said they support the use of blockchain technology for tracking payments.
Is there a legal and legitimate way to invest in bitcoin?
Bitcoin exchanges have a checkered history. Mt.Gox, once the largest exchange, shut down in 2014 after losing hundreds of millions of dollars worth of bitcoin after a hack.
Today, the leading exchange is offered by Coinbase, a startup that has raised more than $200 million from a number of top tier venture capital firms. Square ( SQ ) , the payments service, is also rolling out a bitcoin product.
There are also bitcoin ATMs in scattered bodegas and convenience stores around the country, through companies like Coinsource. The ATMs let you exchange bitcoin for cash, or vice versa by scanning a QR code from the digital wallet application on your phone.
With Coinbase, you must first give the app permission to connect to your bank account. As with other stock trading applications, you pay a small fee for each transaction, buying and selling. But the transaction can take significantly longer.
My original $100 bitcoin purchase won’t officially be completed on Coinbase until Friday, more than a week after the transaction. The price I bought it at remains the same, but I won’t be able to sell at the earliest until Friday.
If the price plummets before then, I’m out of luck. No socks for me.
— CNN’s Selena Larson contributed to this report.
Источник
What is bitcoin cash? – CNN
Here is what you have to know concerning the bitcoin cousin that is quickly rising in recognition.
Related articles
New crypto mining data centres to use 1 GW of Texas renewables
JPMorgan Issues Stark Bitcoin Warning As Ethereum, Binance’s BNB, Cardano And Dogecoin Slide
“Bitcoin money is the model of bitcoin that applied a rise within the transaction capability,” digital foreign money economist Alex de Vries advised CNN Enterprise.
The bitcoin money creators aimed to lift bitcoin’s block measurement restrict of 1 megabyte each 10 minutes — which interprets to a most of seven transactions per second — to eight megabytes each 10 minutes, de Vries stated. Bitcoin money blocks can go as much as 32 megabytes.
The creators of bitcoin money, “wrote an replace for the Bitcoin software program which elevated the transaction restrict,” de Vries stated, and thus, the brand new cryptocurrency was born.
What is the distinction between bitcoin money and bitcoin?
Though each have 18.7 million digital cash within the universe, demand is not practically the identical for bitcoin money as for bitcoin: One coin of bitcoin prices about $57,168 proper now, and one coin of bitcoin money prices about $1,412.
“Bitcoin money has confirmed itself to be one of the vital resilient cryptocurrencies within the digital foreign money ecosystem at this time,” Konstantin Anissimov, govt director of worldwide cryptocurrency trade CEX.IO, advised CNN Enterprise.
Bitcoin money was alleged to boast quicker transaction speeds than bitcoin, however that that did not precisely pan out the best way the creators anticipated. Bitcoin money transaction affirmation occasions stay greater than bitcoin transaction affirmation occasions for a number of sophisticated causes. Nonetheless, bitcoin money has a definite benefit over bitcoin: It is cheaper to make use of.
Prepared to purchase bitcoin money?
Bitcoin money has shot up greater than 139% up to now month. It is comparatively low-cost per coin in comparison with different widespread cryptocurrencies corresponding to ethereum and the unique bitcoin, nevertheless it’s pricier than meme-turned-cryptocurrency dogecoin, which is presently solely $0.60 per coin.
Источник
Bitcoin
Enjoyed the article? Share:
Bitcoin is a decentralized digital currency created by an unknown person or group of people under the name Satoshi Nakamoto and released as open-source software in 2009. It does not rely on a central server to process transactions or store funds.
There are a maximum of 2,099,999,997,690,000 Bitcoin elements (called Satoshis, the unit has been named in collective homage to the original creator), which are currently most commonly measured in units of 100,000,000 known as BTC. There will only ever be 21 million Bitcoin (BTC) to ever be created.
As of January 2018, it is the most widely used alternative currency, now with the total market cap around 250 billion US dollars.
Bitcoin has no central issuer; instead, the peer-to-peer network regulates Bitcoins, transactions and issuance according to consensus in network software. These transactions are verified by network nodes through the use of cryptography and recorded in a public distributed ledger called a blockchain.
Bitcoins are issued to various nodes that verify transactions through computing power. It is established that there will be a limited and scheduled release of no more than 21 million BTC worth of coins, which will be fully issued by the year 2140.
Bitcoins are created as a reward for a process known as mining. They can be exchanged for other currencies, products, and services. As of February 2015, CoinJolt provided over 100,000 merchants and vendors accepted Bitcoin as payment. Research produced by the University of Cambridge estimates that in 2017, there were 2.9 to 5.8 million unique users using a cryptocurrency wallet, most of them using Bitcoin.
Internationally, Bitcoins can be exchanged and managed through various websites and software along with physical banknotes and coins.
Contents
Basic Concepts [ edit ]
Currency [ edit ]
Alice wants to buy alpaca socks which Bob has for sale. In return, she must provide something of equal value to Bob. The most efficient way to do this is by using a medium of exchange that Bob accepts which would be classified as currency. Currency makes trade easier by eliminating the need for coincidence of wants required in other systems of trade such as barter. Currency adoption and acceptance can be global, national, or in some cases local or community-based.
Banks [ edit ]
Alice doesn’t necessarily need to be in direct contact with bob in order for the funds to be transferred. She may instead transfer this value by first entrusting her currency to a bank who promises to store and protect Alice’s currency notes. The bank gives Alice a written promise (called a «bank statement») that entitles her to withdraw the same number of currency bills that she deposited. Since the money is still Alice’s, she is entitled to do with it whatever she pleases, and the bank (like most banks), for a small fee, will do Alice the service of passing on the currency bills to Bob on her behalf. This is done by Alice’s bank by giving the dollar bills to Bob’s bank and informing them that the money is for Bob, who will then see the amount the next time he checks his balance or receives his bank statement.
Since banks have many customers, and bank employees require money for doing the job of talking to people and signing documents, banks in recent times have been using machines such as ATMs and web servers that do the job of interacting with customers instead of paid bank employees. The task of these machines is to learn what each customer wants to do with their money and, to the extent that it is possible, act on what the customer wants (for example, ATMs can hand out cash). Customers can always know how much money they have in their accounts, and they are confident that the numbers they see in their bank statements and on their computer screens accurately reflect the number of dollars that they can get from the bank on demand. They can be so sure of this that they can accept those numbers in the same way they accept paper banknotes (this is similar to the way people started accepting paper dollars when they had been accepting gold or silver).
Such a system has several disadvantages:
- It is costly. EFTs in Europe it can cost up to 25 euros. Credit transactions may cost a significant proportion of the transaction in place.
- It is slow. Checking and low-cost wire services take days to complete.
- In most cases, it cannot be anonymous.
- Accounts can be frozen, or their balance partially or wholly confiscated.
- Banks and other payment processors like PayPal, Visa, and Mastercard may refuse to process payments for certain legal entities.
Bitcoin is a system of owning and voluntarily transferring amounts of so-called bitcoins, in a manner similar to online banking, but pseudonymously and without reliance on a central authority to maintain account balances. If bitcoins are valuable, it is because they are useful and limited in supply.
Bitcoin Basics [ edit ]
Buying Bitcoin [ edit ]
How to buy Bitcoin? There are many ways to buy Bitcoin cryptocurrency, with debit or credit card, PayPal, online on cryptocurrency exchange, with bank transfers and etc. It’s difficult to say what is the best way to buy Bitcoin. After the opening Bitcoin address-account you can start buying coins.
Buying and selling coins to individuals is carried on specialized sites, such as LocalBitcoins. User should select the country and the city in the special window, fill in the information on the number of coins and select the purchase payment method.
Seller should be chosen according to the grade level on the site. Purchasing Bitcoins at the unaccredited sites or from individuals is not recommended due to the high fraud risk.
Creation of coins [ edit ]
The creation of coins must be limited for the currency to have any value.
New coins are slowly mined into existence by following a mutually agreed-upon set of rules. A user mining bitcoins is running a software program that searches tirelessly for a solution to a very difficult math problem whose difficulty is precisely known. The difficulty is automatically adjusted regularly so that the number of solutions found globally, by everyone, for a given unit of time is constant: an average of 6 per hour. When a solution is found, the user may tell everyone of the existence of this newly found solution, along with other information, packaged together in what is called a «block».
Blocks create 12.5 new bitcoins at present. This amount, known as the block reward, is an incentive for people to perform the computation work required for generating blocks. Every 210,000 new blocks generated (roughly every 4 years), the number of bitcoins that can be «mined» in a block reduces by 50%. Originally the block reward was 50 bitcoins; it halved in November 2012 and then once more in July 2016. Any block that is created by a malicious user that does not follow this rule (or any other rules) will be rejected by everyone else. In the end, no more than 21 million bitcoins will ever exist.
Because the block reward will decrease over the long term, miners will some day instead pay for their hardware and electricity costs by collecting transaction fees. The sender of money may voluntarily pay a small transaction fee which will be kept by whoever finds the next block. Paying this fee will encourage miners to include the transaction in a block more quickly.
Bitcoin Mining [ edit ]
Bitcoin Mining is the process of adding transaction records to Bitcoin’s public ledger of past transactions (and a mining rig is a colloquial metaphor for a single computer system that performs the necessary computations for mining). This ledger of past transactions is called the block chain as it is a chain of blocks. The block chain serves to confirm transactions to the rest of the network as having taken place. Bitcoin nodes use the block chain to distinguish legitimate Bitcoin transactions from attempts to re-spend coins that have already been spent elsewhere.
Bitcoin mining’ is intentionally designed to be resource-intensive and difficult so that the number of blocks found each day by miners remains steady. Individual blocks must contain a proof of work to be considered valid. This proof of work is verified by other Bitcoin nodes each time they receive a block. Bitcoin uses the hashcash proof-of-work function.
The primary purpose of mining is to allow Bitcoin nodes to reach a secure, tamper-resistant consensus. Bitcoin Mining is also the mechanism used to introduce Bitcoins into the system: Miners are paid any transaction fees as well as a subsidy of newly created coins. This both serves the purpose of disseminating new coins in a decentralized manner as well as motivating people to provide security for the system.
Bitcoin mining is so called because it resembles the mining of other commodities: it requires exertion and it slowly makes new currency available at a rate that resembles the rate at which commodities like gold are mined from the ground.
Sending payments [ edit ]
To guarantee that a third-party, let’s call her Eve, cannot spend other people’s bitcoins by creating transactions in their names, Bitcoin uses public key cryptography to make and verify digital signatures. In this system, each person, such as Alice or Bob, has one or more addresses each with an associated pair of public and private keys that they may hold in a wallet. Only the user with the private key can sign a transaction to give some of their bitcoins to somebody else, but anyone can validate the signature using that user’s public key.
Suppose Alice wants to send a bitcoin to Bob.
- Bob sends his address to Alice.
- Alice adds Bob’s address and the amount of bitcoins to transfer to a message: a ‘transaction’ message.
- Alice signs the transaction with her private key, and announces her public key for signature verification.
- Alice broadcasts the transaction on the Bitcoin network for all to see.
(Only the first two steps require human action. The rest is done by the Bitcoin client software.)
Looking at this transaction from the outside, anyone who knows that these addresses belong to Alice and Bobcan see that Alice has agreed to transfer the amount to Bob, because nobody else has Alice’s private key. Alice would be foolish to give her private key to other people, as this would allow them to sign transactions in her name, removing funds from her control.
Later on, when Bob wishes to transfer the same bitcoins to Charlie, he will do the same thing:
- Charlie sends Bob his address.
- Bob adds Charlie’s address and the amount of bitcoins to transfer to a message: a ‘transaction’ message.
- Bob signs the transaction with his private key, and announces his public key for signature verification.
- Bob broadcasts the transaction on the Bitcoin network for all to see.
Only Bob can do this because only he has the private key that can create a valid signature for the transaction.
Eve cannot change whose coins these are by replacing Bob’s address with her address, because Alice signed the transfer to Bob using her own private key, which is kept secret from Eve, and instructing that the coins which were hers now belong to Bob. So if Charlie accepts that the original coin was in the hands of Alice, he will also accept the fact that this coin was later passed to Bob, and now Bob is passing this same coin to him.
Preventing double-spending [ edit ]
The process described above does not prevent Alice from using the same bitcoins in more than one transaction. The following process does; this is the primary innovation behind Bitcoin.
- Details about the transaction are sent and forwarded to all or as many other computers as possible.
- A constantly growing chain of blocks that contains a record of all transactions is collectively maintained by all computers (each has a full copy).
- To be accepted in the chain, transaction blocks must be valid and must include proof-of-work (one block generated by the network every 10 minutes).
- Blocks are chained in a way so that, if any one is modified, all following blocks will have to be recomputed.
- When multiple valid continuations to this chain appear, only the longest such branch is accepted and it is then extended further.
When Bob sees that his transaction has been included in a block, which has been made part of the single longest and fastest-growing blockchain (extended with significant computational effort), he can be confident that the transaction by Alice has been accepted by the computers in the network and is permanently recorded, preventing Alice from creating a second transaction with the same coin. In order for Alice to thwart this system and double-spend her coins, she would need to muster more computing power than all other Bitcoin users combined.
Anonymity [ edit ]
When it comes to the Bitcoin network itself, there are no «accounts» to set up, and no e-mail addresses, user-names or passwords are required to hold or spend bitcoins. Each balance is simply associated with an address and its public-private key pair. The money «belongs» to anyone who has the private key and can sign transactions with it. Moreover, those keys do not have to be registered anywhere in advance, as they are only used when required for a transaction. Transacting parties do not need to know each other’s identity in the same way that a store owner does not know a cash-paying customer’s name.
A Bitcoin address mathematically corresponds to a public key and looks like this:
Each person can have many such addresses, each with its own balance, which makes it very difficult to know which person owns what amount. In order to protect his privacy, Bob can generate a new public-private key pair for each individual receiving transaction and the Bitcoin software encourages this behavior by default. Continuing the example from above, when Charlie receives the bitcoins from Bob, Charlie will not be able to identify who owned the bitcoins before Bob.
Capitalization / Nomenclature [ edit ]
Since Bitcoin is both a currency and a protocol, capitalization can be confusing. Accepted practice is to use Bitcoin (singular with an upper case letter B) to label the protocol, software, and community, and bitcoins (with a lower case b) to label units of the currency.
Bitcoin Halving [ edit ]
Bitcoin halving — is a process when every 210 000 blocks (approximately every four years) Bitcoin’s extraction complexity is increased (new coins begin to appear two times slower), and the reward for miners is reduced [1] .
Bitcoin price [ edit ]
The price of BTC token or Bitcoin is always chaining, however, BitcoinWiki gives you a chance to see the prices online on Coin360 widget.
Where to see and explore [ edit ]
You can directly explore the system in action by visiting Biteasy.com, Blockchain.info, Blokr.io Bitcoin Block Explorer or Bitcoin Block Explorer. This last site will show the latest blocks in the blockchain. The blockchain contains the agreed history of all transactions that took place in the system. Note how many blocks were generated in the last hour, which on average will be 6. Also notice the number of transactions; in just one hour there are between 6000 to 7000 transactions. This indicates how active the system currently is.
Next, navigate to one of these blocks. The block’s hash begins with a run of zeros. This is what made creating the block so difficult; a hash that begins with many zeros is much more difficult to find than a hash with few or no zeros. The computer that generated this block had to try many Nonce values (also listed on the block’s page) until it found one that generated this run of zeros. Next, see the line titled Previous block. Each block contains the hash of the block that came before it. This is what forms the chain of blocks. Now take a look at all the transactions the block contains. The first transaction is the income earned by the computer that generated this block. It includes a fixed amount of coins created out of «thin air» and possibly a fee collected from other transactions in the same block.
Drill down into any of the transactions and you will see how it is made up of one or more amounts coming in and out. Having more than one incoming and outgoing amount in a transaction enables the system to join and break amounts in any possible way, allowing for any fractional amount needed. Each incoming amount is a past transaction (which you can also view) from someone’s address, and each outgoing amount is addressed to someone and will be part of a future transaction (which you can also navigate down into if it has already taken place.)
Finally you can follow any of the addresses links and see what public information is available for them.
To get an impression of the amount of activity on the Bitcoin network, you might like to visit the monitoring websites Bitcoin Monitor and Bitcoin Watch. The first shows a real-time visualization of events on the Bitcoin network, and the second lists general statistics on the amount and size of recent transactions.
How many people use Bitcoin? [ edit ]
This is quite a difficult question to answer accurately. One approach is to count how many bitcoin clients connected to the network in the last 24 hours. We can do this because some clients transmit their addresses to the other members of the network periodically. In September 2011 this method suggested that there were about 60,000 users.
White Paper [ edit ]
Bitcoin WhitePaper (WP) is a document that helps your prospective customer make an informed decision in favor of your company or a specific product. If the document does not facilitate a decision, it may be anything but not WP. Speaking in the most understandable language, white paper is something between an article and an advertising brochure. The document contains quite useful information and at the same time leads to the fact that the best solution is to purchase a certain product or service.
You can read English (Original) Bitcoin White Paper here.
Источник