- Pool майнинг Chia Coin
- Технические и экономические особенности
- Pool miner Chia Coin и соло-майнинг
- Как майнить чиа на пул
- Выбор пула для майнинга Chia Coin
- Pool настройка chia
- Pools in Chia
- Chia pool open source
- Launching GitHub Desktop
- Launching GitHub Desktop
- Launching Xcode
- Launching Visual Studio Code
- Latest commit
- Git stats
- Files
- README.md
Pool майнинг Chia Coin
- Технические и экономические особенности
- Pool miner Chia Coin и соло-майнинг
- Как майнить чиа на пул
- Выбор пула для майнинга Chia Coin
- Pool настройка chia
- Преимущества и недостатки майнинга чиа
- Преимущества майнинга монеты chia по сравнению с другими криптовалютами:
- С технической точки зрения преимущества тоже есть:
- Недостатки:
- С технической точки зрения существенные недостатки:
Как майнить чиа на пуле? При майнинге криптовалюты многие присоединяются к существующим майнинговым пулам (то есть ко многим фермерам Chia, работающим вместе, чтобы выиграть Chia Coin «XCH»), чтобы увеличить свои шансы на выигрыш этой криптовалюты.
Технические и экономические особенности
Несмотря на сходство с Bitcoin по некоторым параметрам, код Chia полностью написан с нуля и не использует кодовую базу биткоина.
Для снижения волатильности монеты Chia будет использовать стратегический резерв, созданный в результате пре-фарминга. Своими целями разработчики ставят следующие направления: создание идеального блокчейна для развертывания приложений, образование первой публично торгуемой криптовалюты, близкой к ETF, стимулирования внедрения в корпорациях и среди конечных пользователей. Из-за востребованности Chia (XCH) местами существенно выросли цены на жесткие диски.
Проект не планирует проводить ICO, вместо этого он выйдет на фондовую биржу — проведет IPO, соответствующее требованиям SEC.
После пре-фарминга Chia будет каждые 10 минут предлагать вознаграждение 64 XCH. На протяжении двенадцати лет после запуска каждые три года будет проводиться халвинг (сокращение награды вдвое), затем вознаграждение будет бесконечно оставаться на одном уровне (4 XCH каждые 10 минут). Это сделано, чтобы цена Chia Coin как можно меньше подвергалась инфляции.
Читайте также: Перспективные криптовалюты для инвестирования в 2021 году
Pool miner Chia Coin и соло-майнинг
Как фармить chia на пуле? Алгоритмы Chia противостоят добыче монет с помощью ASIC-устройств, а протокол, открывающий добычу в пулах, пока не был представлен разработчиками. Единственный способ ‒ соло-майнинг, или самостоятельная добыча криптовалюты.
Услуги добычи в группе предлагает HPool.
Полностью избежать появления специализированных устройств на майнинговом рынке не удалось — место ASICов заняли специализированные SSD для добычи Chia, производство которых уже ведется в Китае.
Недостатком соло-майнинга считается медлительность обработки блоков, значит, добычи монет, по сравнению с пулом для коллективной добычи chia. Конкуренция среди добытчиков растет, значит, процесс будет требовать подключения все большего числа жестких дисков. При этом на рынке наблюдается дефицит накопителей, вызванный майнерами, и рост цен на диски, которые еще есть в доступе, что означает двойной рост затрат.
Chia по-прежнему находится на стадии бета-тестирования, а обналичивание монет или их обмен на криптовалютных биржах недоступен. При текущих расходах майнеров курс Chia должен составлять порядка $ 3,4.
На бирже Hotbit ведутся торги так называемыми IOU, или долговыми расписками Chia. Курс Chia по ним на конец апреля составляет здесь около $ 1,300. Это дает приблизительное понимание того, как стартуют торги реальными монетами. Учитывать стоит тот факт, что по сравнению с IOU цены на криптовалюту могут оказаться ниже в несколько раз.
Как майнить чиа на пул
Если мощность фермы с дисками HDD или SSD небольшая, то можно добывать валюту на пуле — объединении мощностей группы майнеров. Награда с пула зачисляется на кошелек каждого участника пула, ее величина зависит от мощности фермы участника. Принцип работы chia криптовалютаы pool такой: майнеры объединяют мощности и вычисляют блок в блокчейне Chia, награда делится между всеми.
Выбор пула для майнинга Chia Coin
Pool настройка chia
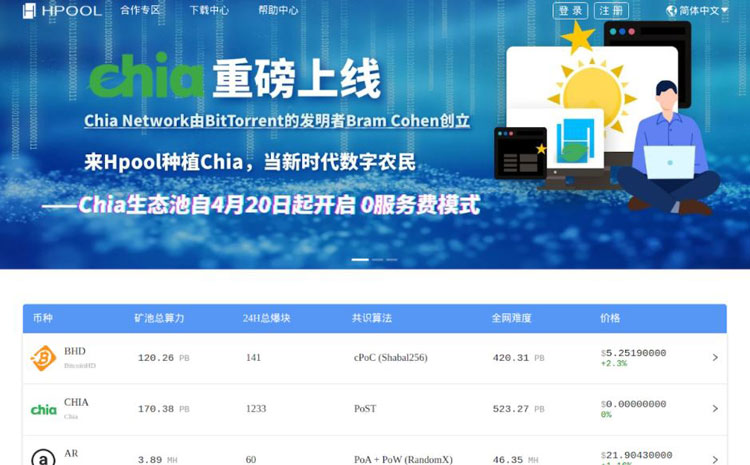
Работающие пулы можно посмотреть на сайте miningpoolstats.stream/chia. Главный критерий выбора — общий хешрейт.
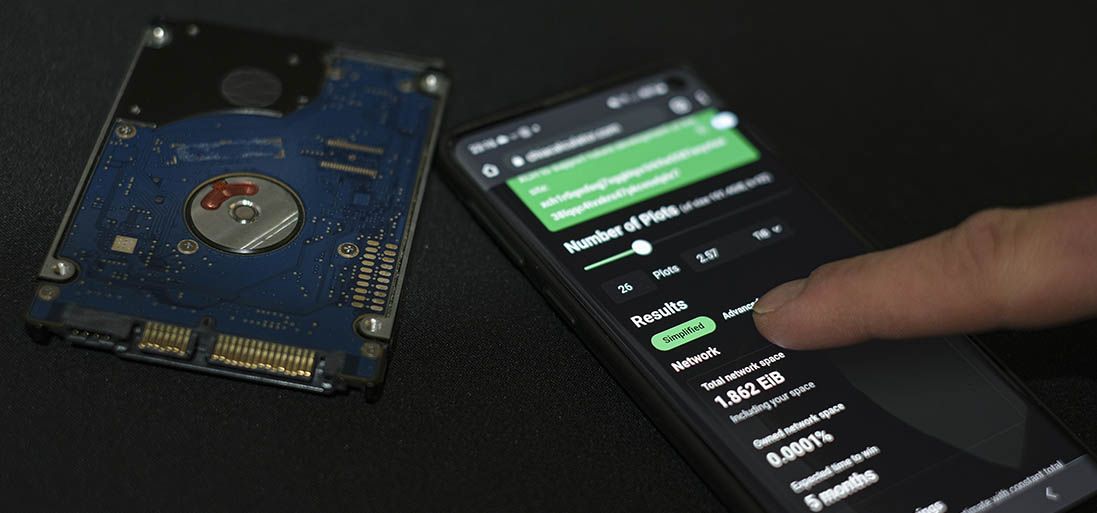
Chia как подключиться к пулу? Необходимо выбрать пул, который занимает как можно больше процентов мощности сети (hpool.com) — он будет находить больше блоков, поэтому наиболее выгоден. Необходимо перейти на его сайт и зарегистрироваться на пуле. Регистрация стандартная — после ввода данных на электронную почту придет письмо с подтверждением и необходимо перейти по подтверждающей ссылке.
После входа в свой аккаунт необходимо зайти в раздел Personal Center для добавления верификации от Google. Чтобы это сделать, необходимо установить на телефон соответствующее приложение.
Затем нужно установить верификацию по СМС, но этот пул не работает с номерами России и Украины, обойти это можно, заведя виртуальный номер на специальных сервисах. После установки верификации появится возможность вписать свой кошелек, на который будут зачисляться монеты Chia.
Чтобы отслеживать mining Hpool stats chia (статистику), необходимо перейти в раздел Pool, пункт Open Pool, вы увидите сниппет. Кликаем на Pool Details. Вы увидите полную статистику по майнингу Chia Coin на пуле Hpool.
Затем необходимо в разделе Download Center скачать приложение — Chia-плоттер. Ссылка ведет на GitHub, где необходимо найти последнюю версию плоттера и выбрать для скачки файл, имя которого начинается на «chia-plotter-gui» для вашей операционной системы.
Скачанную программу нужно запустить, ее интерфейс на китайском языке, но это не проблема, т.к. у нее мало элементов. В самое верхнее поле ввода нужно ввести мнемоническую фразу от кошелька (должно быть 24 слова) и нажать на кнопку Sign, которая запускает авторизацию кошелька в блокчейне. Затем можно сравнить номер своего кошелька и появившийся номер в программе после авторизации, если они совпадают, значит, все нормально.
В левой части окна программы находится вертикальное меню, в нем нужно выбрать раздел Pool, в нем подраздел open Pool и нажать на кнопку All, что в верхней части окна.
Отобразится список пулов, необходимо найти пул с названием CHIAECO и нажать на кнопку Open Pool, которая внизу блока с информацией. Состоится переход на страницу с этим пулом, где необходимо нажать на кнопку Go To Configuration — откроется раздел, где в поле для ввода необходимо скопировать сигнатуру, полученную при запуске программы плоттера.
При этом приложение попросит скопировать код из Гугл аутентификатора, после его ввода появится номер кошелька Chia под заголовком Binding Check, у него должен быть статус Successful. Значит, кошелек добавлен на пул.
Источник
Pools in Chia
— November 10, 2020
Update: Check the Pooling FAQ for more updates.
As the launch of Chia’s mainnet approaches I want to go over the current status of farmer pools in Chia and what the plans for pooling are in the future.
TL;DR We don’t have pooling fully implemented yet but are building in hooks to make two approaches to farmer pools work well in the future.
We’re approaching pooling support in Chia with caution because they’re a large potential source of centralization in a system which we’re designing to be as decentralized as possible. That said, there are some real benefits to pools: They smooth out farming rewards, especially for small farmers, and they can ensure that good timelord infrastructure is being run. Even so, we recommend that farmers self-pool and have taken steps to make self-pooling as painless as possible. Additionally, in our new consensus algorithm there are 32 times as many reward events per day as there are in Bitcoin. With 4608 chances to win 2 chia each day, we think that even small farmers with self pools will be able to win rewards over reasonable time frames in the early months of mainnet. (Updated February 2021 to modify that it will be 4608 chances to win 2 chia each day.)
That said, it does make sense to use pools in some circumstances so we’re building in hooks for them with certain intended protocols in mind. First and foremost, even when a winning farmer is using a pool, they themselves are the ones who make the transaction block — not the pool. The decentralization benefits of this policy are obvious. To maximize the attractiveness and stability of this method, all the transaction fees generated by a block go to the farmer who found it and not to the pool.
Trying to split the transaction fees with the pool could result in transaction fees being paid ‘under the table’ either by making them go directly to the farmer or making an anyone can spend output which the farmer would then pay to themselves. Circumventing the pool would take up space on the blockchain. It could also encourage the emergence of alternative pooling protocols where the pool makes the transaction block which is a form of centralization we wish to avoid. This method has the downside of reducing the smoothing benefits of pools if transaction fees come to dominate fixed block rewards. That’s never been a major issue in Bitcoin and our block reward schedule is set to only halve three times and continue at a fixed amount forever after. There will alway be block rewards to pay to the pool while transaction fees go to the individual farmers.
Possibly the most debatable part of our planned pooling protocol is that fixed block rewards are set to go 7/8 to the pool and 1/8 to the farmer. This seems to be a sweet spot where it doesn’t reduce smoothing all that much but also wipes out potential selfish mining attacks where someone joins a competing pool and takes their partials but doesn’t upload actual blocks when they find them. Those sort of attacks can become profitable when the fraction of the split is smaller than the size of the pool relative to the whole system. We have the option to change this split before mainnet launch and are open to feedback and opinions about it — which I’m sure people will have. Please be polite.
When farmers make the blocks there is an auditing problem for pools. The pools need to be able to ensure that a farmer doesn’t claim partials from multiple pools or steal whole block rewards when they find them. The simplest way to do this is to have separate pool keys in plot files which sign where the rewards go. This was the first thing we built in the interests of being able to guarantee that current plot files would work on mainnet as early as possible.
This approach allows anyone to join a pool without having prior interaction with either the pool or the blockchain. The downside of this approach is that once you start using a pool you can’t switch without redoing your plots. Our testnet farming community has explained that it’s highly desirable to also have a pooling protocol which allows for switching pools without having to redo plots. I’ve come up with a plan for how to support that.
The new hook for supporting pool switching is an alternative plot format which contains a puzzle hash. A puzzle hash determines how a coin can be spent. It’s the Chia equivalent of what’s called a scriptpubkey in Bitcoin. Pool block rewards are sent to that puzzle instead of there being a pool public key which signs where each reward goes. You might be wondering what this has to do with pool switching. A common theme with Chialisp, our on-chain programming environment, is that the tools look insufficient for doing what you want but are actually capable of doing it in a much more robust and versatile way than more specialized tools could. The next paragraph explains this, but is a bit technical, so feel free to skip.
In order to support pool switching there needs to be some kind of on chain state which determines where a given farmer’s rewards are going which is both auditable by the pool and changeable by the farmer. We have a policy that the only on chain state is the current coin set. Using the combined tricks of backwards pointing covenants as capabilities and hiding state in puzzle hashes we can implement singletons. A given farmer’s singleton needs to have a puzzle which follows a standard template so that the pool can verify that it’s there and can use it to claim farming rewards. That singleton can also have functionality to change what pool it’s pointed at but there needs to be a grace period before the change takes effect during which the old pool can still use it to claim block rewards to keep the farmer from stealing.
This sounds like a complicated bunch of different technologies but we’ve already built several smart transactions which use these primitives in much more sophisticated ways. This approach allows full flexibility for pools to set the parameters for when and how pool switching is done.
The downside of this approach is that it requires posting transactions to the blockchain in order to start using a pool or to switch pools. This incurs transaction fees and is a privacy leak. Our original, and simpler approach also has extra privacy benefits if pool keys are aggregated between the pool and the farmer.
Fleshing out the details of both pooling protocols is beyond the scope of this post and will require real work to complete. We’re planning on supporting both in the future but releasing mainnet is a higher priority right now so please be understanding of our choice to keep our resources focused on launch.
It is always possible for an existing pool to start supporting new protocols and smooth out rewards across all of the protocols so there’s a clean upgrade path for them to support simpler protocols now and expand to more sophisticated protocols later.
It’s impossible to be all things to all people. In this case we’ve made the decision to support pooling in ways which are consistent with how everything else in Chia is done and doesn’t cause ongoing difficulties for a single use case. The downside is that plots being made today won’t be able to switch pools in the future without replotting. For that we are sorry. But we promise that plots of k=32 or larger made today will work on mainnet and continue to do so well into the future.
Источник
Chia pool open source
Use Git or checkout with SVN using the web URL.
Work fast with our official CLI. Learn more.
Launching GitHub Desktop
If nothing happens, download GitHub Desktop and try again.
Launching GitHub Desktop
If nothing happens, download GitHub Desktop and try again.
Launching Xcode
If nothing happens, download Xcode and try again.
Launching Visual Studio Code
Your codespace will open once ready.
There was a problem preparing your codespace, please try again.
Latest commit
Git stats
Files
Failed to load latest commit information.
README.md
This prototype is not yet supported and is still in development. This code is provided under the Apache 2.0 license. Note: the draft specification is in the SPECIFICATION.md file.
Several things are customizable in this pool reference. This includes:
- How long the timeout is for leaving the pool
- How difficulty adjustment happens
- Fees to take, and how much to pay in blockchain fees
- How farmers’ points are counted when paying (PPS, PPLNS, etc)
- How farmers receive payouts (XCH, BTC, ETH, etc), and how often
However, some things cannot be changed. These are described in SPECIFICATION.md, and mostly relate to validation, protocol, and the singleton format for smart coins.
A partial is a proof of space with some additional metadata and authentication info from the farmer, which meets certain minimum difficulty requirements. Partials must be real proofs of space responding to blockchain signage points, and they must be submitted within the blockchain time window (28 seconds after the signage point).
The pool server works by receiving partials from the users, validating that they are correct and correspond to a valid signage point on the blockchain, and then adding them to a queue. A few minutes later, the pool pulls from the queue, and checks that the signage point for that partial is still in the blockchain. If everything is good, the partial is counted as valid, and the points are added for that farmer.
Collecting pool rewards
The pool periodically searches the blockchain for new pool rewards (1.75 XCH) that go to the various p2_singleton_puzzle_hashes of each of the farmers. These coins are locked, and can only be spent if they are spent along with the singleton that they correspond to. The singleton is also locked to a target_puzzle_hash , which in this diagram is the red pool address. Anyone can spend the singleton and the p2_singleton_puzzle_hash coin, as long as it’s a block reward, and all the conditions are met. Some of these conditions require that the singleton always create exactly 1 new child singleton with the same launcher id, and that the coinbase funds are sent to the target_puzzle_hash .
Calculating farmer rewards
Periodically (for example once a day), the pool executes the code in create_payment_loop . This first sums up all the confirmed funds in the pool that have a certain number of confirmations.
Then, the pool divides the total amount by the points of all pool members, to obtain the mojo_per_point (minus the pool fee and the blockchain fee). A new coin gets created for each pool member (and for the pool), and the payments are added to the pending_payments list. Note that since blocks have a maximum size, we have to limit the size of each transaction. There is a configurable parameter: max_additions_per_transaction . After adding the payments to the pending list, the pool members’ points are all reset to zero. This logic can be customized.
Difficulty adjustment algorithm
This is a simple difficulty adjustment algorithm executed by the pool. The pool can also improve this or change it however they wish. The farmer can provide their own suggested_difficulty , and the pool can decide whether or not to update that farmer’s difficulty. Be careful to only accept the latest authentication_public_key when setting difficulty or pool payout info. The initial reference client and pool do not use the suggested_difficulty .
- Obtain the last successful partial for this launcher id
- If > 3 hours, divide difficulty by 5
- If > 45 minutes
Note that the payout info is provided with each partial. The user can choose where rewards are paid out to, and this does not have to be an XCH address. The pool should ONLY update the payout info for successful partials with the latest seen authentication key for that launcher_id.
Install and run (Testnet)
To run a pool, you must use this along with a branch of chia-blockchain .
Checkout the pools.2021-may-25 branch of chia-blockchain , and install it. Checkout this repo in another directory next to (not inside) chia-blockchain . Make sure to be on testnet by doing export CHIA_ROOT=».chia/testnet7″ and chia configure —testnet true .
Create two keys, one which will be used for the block rewards from the blockchain, and the other which will receive the pool fee that is kept by the pool.
Change the wallet_fingerprint and wallet_id in the config.yaml config file, using the information from the first key you created in step 2. These can be obtained by doing chia wallet show .
Do chia keys show and get the first address for each of the keys created in step 2. Put these into the config.yaml config file in default_target_puzzle_hash and pool_fee_puzzle_hash respectively.
Change the pool_url in pool.py to point to your external ip or hostname. This must match exactly with what the user enters into their UI or CLI, and must start with https://. For now http:// can also be used.
If you would like to test with smaller plots (instead of using k32s), go to the file default_constants.py and increase POOL_SUB_SLOT_ITERS from 37600000000 to 37600000000 * (2**11). The default value with difficulty 1 (the lowest) will result in 10 partials per day per k32. This makes it difficult to test due to large plots.
Start the node using chia start farmer , and log in to a different key (not the two keys created for the pool). This will be referred to as the farmer’s key here. Sync up your wallet on testnet for the farmer key.
Create a venv (different from chia-blockchain) and start the pool server using the following commands:
You should see something like this when starting, but no errors:
Create a pool nft (on the farmer key) by doing chia plotnft create -u http://127.0.0.1:80 , or whatever host:port you want to use for your pool. Approve it and wait for transaction confirmation. This url must match exactly with what the pool uses.
Do chia plotnft show to ensure that your plotnft is created. Now start making some plots for this pool nft. You can make plots by specifying the -c argument in chia plots create . Make sure to not use the -p argument. The value you should use for -c is the P2 singleton address from chia plotnft show output. You can start with small k25 plots and see if partials are submitted from the farmer to the pool server. The output will be the following in the pool if everything is working:
Note that switching pools is still not enabled, but will be added very shortly. Please send a message to @sorgente711 on keybase if you have questions about the 10 steps explained above. All other questions should be send to the #pools channel in keybase. Note that there will probably be breaking changes soon which will require re-plotting and re-running all the steps above.
Источник