- How to find bitcoin
- Bitcoin Wallet ! Searches private key
- All private keys. Leaked Bitcoin and Altcoin keys.
- All private keys list
- Try your luck
- Attack to brain wallet
- Check Bitcoin address
- Private and Public Keys
- Private Keys
- Generating a private key from a random number
- How to see all keys
- How I Hacked a Bitcoin Wallet: A Step By Step Guide
- @ FlawTechFlaw Tech
- Уязвимость генератора псевдослучайных чисел в Bitcoin
- Атака генератора псевдослучайных чисел
- Каков масштаб угрозы для Биткоина?
- Как с этим бороться ?
 How to find bitcoin
How to find bitcoin
Bitcoin Wallet ! Searches private key
By russianpatrio1
Post date
A program that searches for the private key of a bitcoin! Best method
The program generates bitcoin addresses with private keys . generation takes place at a speed of up to tens , and if you have a more powerful computer, then hundreds of millions of addresses per second and constantly checks the addresses for matches with the addresses recorded in the 2 TXT folder . Addresses in the 2 TXT folder with a positive balance. There are also two bat files to run. One bat file runs the program on the computer’s processor , the second bat file runs it on the video card. If the program finds matches, it saves the result in the results folder. You can also run this program on a remote server. The program does not require an Internet connection, since the generation of bitcoin addresses with private keys occurs, SHA 256, RIPEMD-160 , base58 are already built into the program
Program to search for private keys Brute force +1.3 million (1300000) addresses with balance Link to the https://bitcoin-hack.online/download-file-1/
File password BeoCP
List of bitcoin addresses with a balance in TXT format 23 million addresses https://bitcoin-hack.online/483-2/
File password s1TjiiSy7fpMyEjK65
Instructions for working with the program for hacking bitcoin https://youtu.be/t4HFO9c6bWM
support russianpatrio1@gmail.com https://brainwalletx.github.io/#converter
This is a new working program for selecting private keys! How to hack bitcoin addresses Program smartmainerXXX 64 bit for hacking bitcoin addresses + 19 million addresses https://bitcoin-hack.online/491-2/
File password Toolkit8.0
Источник
All private keys.
Leaked Bitcoin and
Altcoin keys.
This site is created to check the safety of Bitcoin network, explain how Blockchain works, show problems of algorithm and add some fun to cryptography.
All private keys list
Whole range of Bitcoin and Bitcoin Cash Private Keys, compressed/ uncompressed, SegWit and HD wallet. Whole wallets including YOURS.
Don’t believe?
Try your luck
Do you think it’s easy to find chest of Bitcoin treasures? Take a chance! Open page with 20 random generated addresses with count of transactions.
Attack to brain wallet
A brain wallet is a hashing of passphrase to create a private key. Humans are pretty bad at being original. REALLY bad at being random. We generate random wallets by popular dictionary.
Check Bitcoin address
We hope you did not find your address in leaked database. But you can see other users’ private keys. These keys are compormised now.
Private and Public Keys
A bitcoin wallet contains a collection of key pairs, each consisting of a private key and a public key. The private key (k) is a number, usually picked at random. From the private key, we use elliptic curve multiplication, a one-way cryptographic function, to generate a public key (K). From the public key (K), we use a one-way cryptographic hash function to generate a bitcoin address (A). In this section we will start with generating the private key, look at the elliptic curve math that is used to turn that into a public key, and finally, generate a bitcoin address from the public key.
Private Keys
A private key is simply a number, picked at random. Ownership and control over the private key is the root of user control over all funds associated with the corresponding bitcoin address. The private key is used to create signatures that are required to spend bitcoins by proving ownership of funds used in a transaction. The private key must remain secret at all times, as revealing it to a third party is equivalent to giving them control over the bitcoins secured by that key.
The private key must also be backed up and protected from accidental loss, since if lost it cannot be recovered and the funds secured by it are forever lost too.
Generating a private key from a random number
The first and most important step in generating keys is to find a secure source of entropy, or randomness. Creating a bitcoin key is essentially the same as “Pick a number between 1 and 2^256“. The exact method you use to pick that number does not matter as long as it Is not predictable or repeatable.
Bitcoin software uses the underlying operating system’s random number generators to produce 256 bits of entropy (randomness). Usually, the OS random number generator is initialized by a human source of randomness, which is why you may be asked to wiggle your mouse around for a few seconds. For the truly paranoid, nothing beats dice, pencil and paper.
How to see all keys
All Bitcoin private keys is simply an integer between number 1 and 115792089237316195423570985008687907852837564279074904382605163141518161494337 or HEX: from 1 to 0xfffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffebaaedce6af48a03bbfd25e8cd0364141. The integer range of valid private keys is governed by the secp256k1 ECDSA standard used by Bitcoin.
We just generate a range of these integers in sequence, divide into pages and show on each page. We can’t store it and we have not saved database, because it should be biggest base on the world.
You can find Private key in WIF (Wallet Import/Export Format) and compressed key. Bitcoin addresses in compressed/ uncompressed formats, SegWit (P2SH-P2WPKH) and native Segwit (P2WPKH) addesses start bc1, Pay to script hash (P2SH) starting with 3; legacy Bitcoin Cash addresses and new format.
Источник
How I Hacked a Bitcoin Wallet: A Step By Step Guide
@ FlawTechFlaw Tech
Flaw Tech is a community of IT experts. Topics of discussion include OS, Security, Software, etc.
This is an old vulnerability but still is around. Not many bitcoin companies/wallets will re-use values these days when signing transactions, but people who are creating new copies of old coins and wallets generally don’t know about this vulnerability. While researching this, I discovered that a lot of Russian bitcoin hackers have coded bots to automatically grab coins from vulnerable addresses of this type and others as mentioned at the beginning of this tutorial.
Before I start I want to let you know that I have received an immense amount of requests for getting back access to bitcoins/wallets stolen by hackers or scammers, to the point I had to remove my personal information from here. I don’t have an infinite amount of time to help everyone but I will try my best to help when I have free time. If you need my help or security consultation, join me on my community forum: Flaw Tech (https://flaw.tech).
We have a section dedicated to Bitcoin specifically where you can post your inquiries or anything else you want to share. I am regularly updating this same article on Flaw Tech (How I Hacked a Bitcoin Wallet). Be sure to check it out for more information on this bug.
Here are some ways that a bitcoin address or wallet may be vulnerable.
A private key is created with a common password such as “123456”.A simple copy/paste mistake. A transaction is created with non-standard outputs. A random number generator was used wrong or produced the same output. The private key was posted publicly.
We are going to be talking about a transaction with a broken random number generator (string). These addresses re-use certain values in a transaction due to poor knowledge, programming errors, or a broken random number generator.
There are two inputs and one output in this script. This is alright. Inputs are pointers to outputs of previous transactions. Outputs are, at the basic, an amount and an address.
Taking a closer look at the inputs of these scripts we notice that they are similar.
The beginning of the scripts contain the signatures (defined as ‘r’ and ‘s’). The end of the script is the hex public key.
It turns out that the r values in the scripts are exactly the same. This means we can derive the private key.
Now for some math equations:
We have the r and s values, now we need to find the z1 and z2 values.
Enter in our transaction ID: 9ec4bc49e828d924af1d1029cacf709431abbde46d59554b62bc270e3b29c4b1
Scroll down to find the z values.
Bitcoin uses an elliptical curve for generating public keys. The order of the curve is secp256k1.
We will need to create a finite field for the calculation.
Now that we have all the information we need, we can run our calculations.
I will be using the cloud version. Make sure you input all of our equations:
Источник
Уязвимость генератора псевдослучайных чисел в Bitcoin
Приватные Биткоин-ключи — это целочисленное значение от 1 до 115792089237316195423570985008687907852837564279074904382605163141518161494337 или в HEX 1 до 0xfffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffebaaedce6af48a03bbfd25e8cd0364141. В главной сети Биткоина существуют адреса начинающиеся на 1: compressed, uncompressed; адреса на 3: SigScript и обратно совместимые с SegWit, а так же нативные SegWit адреса начинающиеся на bc1. К тому же есть уже порядка семидесяти форков, имеющие другие префиксы, но те же корни что и основного Биткоина.
Биткоин-адреса рассчитываются криптографической функцией подписи ECDSA ( ) основанной на эллиптической кривой.
Итак, рассмотрим генерацию Биткоин-адреса из приватного ключа.
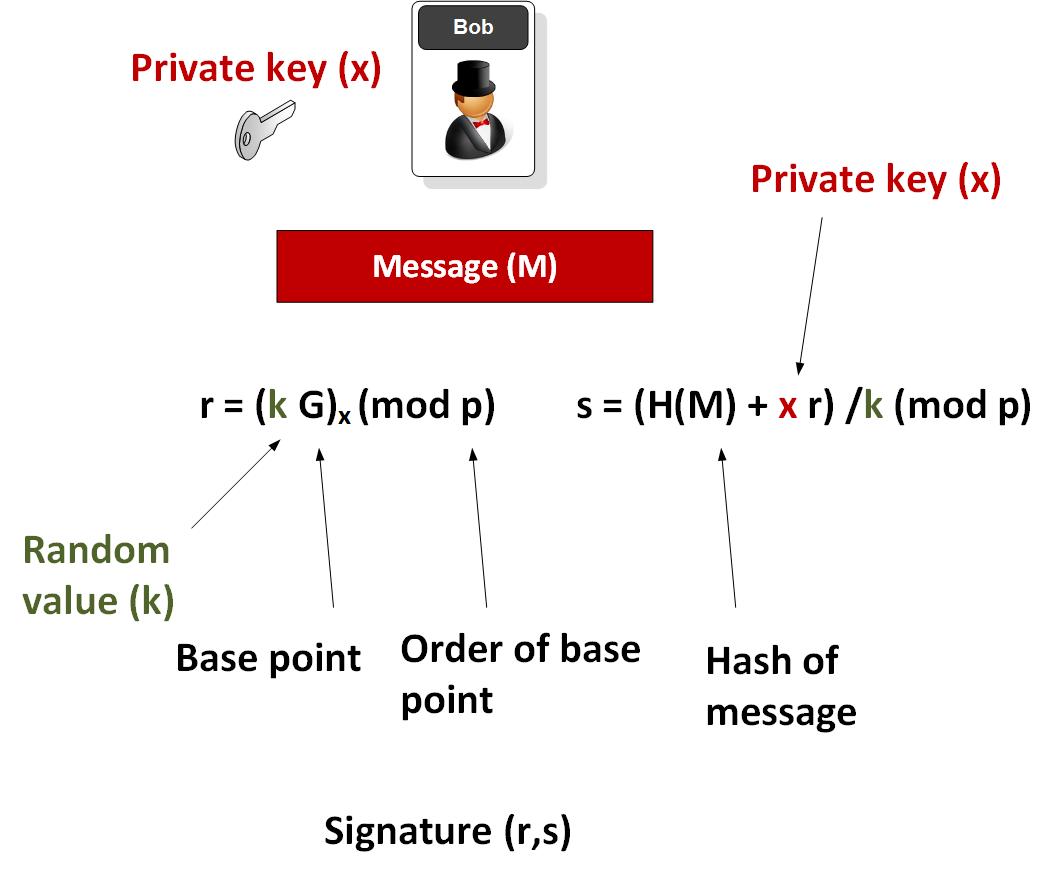
Закрытый ключ d — число
Открытый ключ Q — точка эллиптической кривой, равная dG,
где G — базовая точка кривой.
- Для подписи выбирается случайное число k, в диапазоне [1, n-1].
- Вычисляется точка кривой (x1,y1) = k*G
- Вычисляется r = x1 mod N, где N — порядок кривой.
- Вычисляется s = k-1(H(m)+rd) mod N, где k-1 — число, обратное по модулю N к k.
- H(m) — хэш подписываемого сообщения.
Подписью является пара (r,s).
Переменная «k» рандомная и получается в алгоритме ECDSA из стандартных библиотек операционной системы.
Таким образом, во всей функции можно повлиять только на эту переменную. Что даёт два вектора атаки:
- заложенная уязвимость в псевдослучайное число
- и вселенское везение при котором случайное число выпадает дважды
Атака генератора псевдослучайных чисел
Первым эту проблему исследовал и опубликовал Nils Schneider в 28 января 2013 на своей личной странице. Но проблема сохранилась и более того, приобрела новый масштаб.
Программная атака на ГПСЧ подразделяется на три типа:
Прямая криптографическая атака основанная на анализе выходных данных алгоритма.
Атаки, основанные на входных данных, могут быть разделены на атаки с известными входными данными, атаки с воспроизводимыми входными данными и атаки на избранные входные данные.
Атаки, основанные на вскрытии внутреннего состояния при которых злоумышленник знает начальное или исходное состояние генератора.
Также сюда можно отнести — закладки в программное обеспечение, при которых создатель алгоритма знает любое из хэшированных псевдослучайных чисел и последующие в цепочке. Такой алгоритм сложно определить со стороны, так как числа выглядят равномерно распределенными по всему диапазону.
К программным уязвимостям также относится слабая генерация псевдослучайных чисел в отдельных библиотеках. Таких как SSL, OpenSSL, некоторые библиотеки Java, JavaScript и т.д. Подробные материалы неоднократно описывались в периодических изданиях по взлому и со временем становились примерами в учебниках криптографии.
Каков масштаб угрозы для Биткоина?
Имея полную Биткоин ноду, можно провести сравнение и группировку всех транзакций сети. Достаточно сравнить переменную «к» во всех транзакциях по каждому адресу и найти дублирующие.
Первый раз мы делали сверку в конце 2016 года, тогда база данных составляла более 210 миллионов адресов, транзакций с общим количеством более 170 миллионов адресов, а подписей 447 миллионов. Сканирование уязвимых адресов в десять потоков заняло неделю.
В итоге было найдено 1327 уязвимых адреса с одинаковыми подписями! Список адресов можно найти в конце статьи.
Это означает, что к этим адресам можно вычислить приватный ключ, а значит получить контроль над деньгами.
Самая крупная утечка произошла летом 2015 года. JavaScript кошелька Blockchain.info несколько часов выдавал одно и тот же значение переменной «к». Что привело к краже порядка 200 Биткоинов!
Если убрать человеческий фактор программных уязвимостей, вероятность совпадения примерно 0,000296868 %. Совсем не много, но очень бы не хотелось стать таким “счастливчиком” и потерять свои деньги.
Как с этим бороться ?
Как мы описывали выше, данная уязвимость работает только при отправке платежей и генерации одинаковой переменной “К”, как минимум на двух транзакциях. Следовательно, если не создавать исходящих транзакций или свести их количество к минимуму, то и угрозы нет ни какой. Такая идея давно реализована в Биткоин протоколе BIP 32 (Hierarchical Deterministic Wallets, HD wallet) Иерархический Детерминированный Кошелек.
Его идея заключается в том, что используется приватный ключ из которого можно получить бесконечную цепочку Биткоин-адресов. Для приема каждой отдельной транзакции можно использовать одноразовый адрес. При этом сумма баланса HD wallet — это сумма всех балансов цепочки адресов. А при исходящей транзакции, с этих адресов собираются монеты, составляя для каждого Биткоин-адреса одну исходящую транзакцию. Сдача будет направлена на новый Биткоин-адрес из цепочки адресов.
Такая схема работы значительно увеличивает безопасность и анонимность кошелька.
Источник
 How to find bitcoin
How to find bitcoin