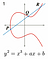- How to Generate a Bitcoin Address — Step by Step
- Introduction
- Dependencies
- Cryptography Primer
- Public Key Cryptography
- Creating a Bitcoin Address
- Private Key Generation
- Public Key Generation
- Compressed Public Key
- Address Generation
- Pay-to-Script Hash
- Bitcoin address
- Contents
- What’s in a Bitcoin address [ edit ]
- Purpose and opportunities [ edit ]
- Input conditions [ edit ]
- How to create Bitcoin address? [ edit ]
- Transactions [ edit ]
- Bitcoin Address Validation [ edit ]
- Loss of Bitcoins [ edit ]
- Multi-signature Bitcoin address [ edit ]
- Address balances [ edit ]
- «From» addresses [ edit ]
How to Generate a Bitcoin Address — Step by Step
Here is a bash script that does what is outlined below: https://bit.ly/2MIgeOD
Introduction
This is a hands-on, technical guide about the generation of Bitcoin addresses including private and public keys, and the cryptography involved.
Learn more and join people in 22 countries around the world in my course on how to Become a Bitcoin + Blockchain Programmer.
This guide will walk you through all the steps to generate a Bitcoin address using the command line on a Mac. Similar steps should be possible on other operating systems using similar cryptographic tools. Lines starting with $ denote terminal commands, which you can type and run (without the $ of course).
Dependencies
- brew — Installation: https://brew.sh/
- pip — Installation: sudo easy_install pip
- libressl — Installation: brew install libressl
- base58 — Installation: pip install base58
Note: To do the contained openssl cli commands, I installed libressl in order for some of the elliptic curve commands to work as the current version of openssl cli on mac has a bug.
Cryptography Primer
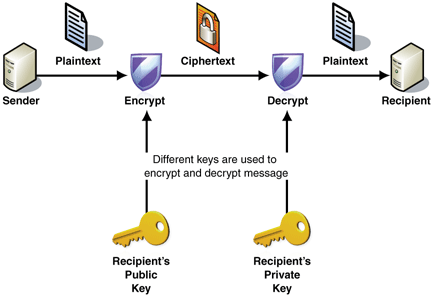
Public Key Cryptography
Or asymmetric cryptography, is a type of cryptography that uses key pairs, each of which is unique. The pair of keys includes a public key and a private key. This is the type of cryptography that Bitcoin uses to control funds. A public key can be generated from a private key, but not vice-versa (computationally too difficult). Also, something encrypted with a private key can be decrypted with the public key, and vice-versa, hence they are asymmetric.
- Encryption: When a user has a public key, a message can be encrypted using a public key, which can only be read by the person with the private key. This also works in reverse.
- Digital Signatures: A user can, with their private key and a hash of some data, use a digital signature algorithm such as ECDSA, to calculate a digital signature. Then, another user can use the algorithm to verify that signature using the public key and the hash of the same data. If it passes, this proves a user did in fact submit a specific message, which has not been tampered with.
- Digital Fingerprint: Is a way to represent an arbitrarily large data set by computing the hash of it to generate a fingerprint of a standard size. This fingerprint would be so difficult to replicate without the same exact data, which can be assumed to have not been tampered with.
Private keys are what prove you can send Bitcoin that has been sent to you. It is like the password to your bank account. If you lose it or someone else gets a hold of it, you’re toast.
Public keys help people know how to send you Bitcoin.
Creating a Bitcoin Address
Private Key Generation
Private keys can be any 256 bit (32 byte) value from 0x1 to 0xFFFF FFFF FFFF FFFF FFFF FFFF FFFF FFFF BAAE DCE6 AF48 A03B BFD2 5E8C D036 4140 .¹
The total possible number of private keys is therefore 2²⁵⁶ or 1.16 x 10⁷⁷. Imagine the total number of atoms in your body, then imagine that each of those atoms is an earth. The total number of atoms on all of those earths is about 7 x 10⁷⁷.² There is virtually no chance that your random private key will ever be generated randomly or found by someone else.
A common (but not the most secure) way of creating a private key is to start with a seed, such as a group of words or passphrases picked at random. This seed is then passed through the SHA256 algorithm, which will always conveniently generate a 256 bit value. This is possible because every computer character is represented by an integer value (see ASCII and Unicode).
Note: SHA256 is a one-way, deterministic function meaning that it is easy to compute in one direction, but you cannot reverse it. In order to find a specific output, you have to try all the possible inputs until you get the desired output (brute forcing) and it will always produce the same output given the same input, respectively.
The seed can be used to generate the same private key if the same hashing algorithm is used in the future, so it is only necessary to save the seed.
This private key is in hexadecimal or base 16. Every 2 digits represents 8 bits or 1 byte. So, with 64 characters, there are 256 bits total.
Public Key Generation
Public keys are generated from the private keys in Bitcoin using elliptic curve ( secp256k1 ) multiplication using the formula K = k * G , where K is the public key, k is the private key, and G is a constant called the Generator Point⁴, which for secp256k1 is equal to:
It doesn’t seem to be known how this point was chosen by they designers of the curve. Also, this algorithm is a one-way algorithm, or a “trap door” function so that a private key cannot be derived from the public key. It is important to note that elliptic curve multiplication is not the same as scalar multiplication, though it does share similar properties.
To do this in the terminal from our private key earlier,
This public key contains a prefix 0x04 and the x and y coordinates on the elliptic curve secp256k1 , respectively.
Compressed Public Key
Most wallets and nodes implement compressed public key as a default format because it is half as big as an uncompressed key, saving blockchain space. To convert from an uncompressed public key to a compressed public key, you can omit the y value because the y value can be solved for using the equation of the elliptic curve: y² = x³ + 7. Since the equation solves for y², the right side of the equation could be either positive or negative. So, 0x02 is prepended for positive y values, and 0x03 is prepended for negative ones. If the last binary digit of the y coordinate is 0, then the number is even, which corresponds to positive. If it is 1, then it is negative. The compressed version of the public key becomes:
The prefix is 0x02 because the y coordinate ends in 0xa4 , which is even, therefore positive.
Address Generation
There are multiple Bitcoin address types, currently P2SH or pay-to-script hash is the default for most wallets. P2PKH was the predecessor and stands for Pay to Public Key Hash. Scripts give you more functionality, which is one reason why they are more popular. We’ll first generate a P2PKH original format address, followed by the now standard P2SH .
The public key from the previous output is hashed first using sha256 and then hashed using ripemd160 . This shortens the number of output bytes and ensures that in case there is some unforeseen relationship between elliptic curve and sha256, another unrelated hash function would significantly increase the difficulty of reversing the operation:
Note that since the input is a string, the xxd -r -p will convert the hex string into binary and then output it in hexdump style (ascii), which is what the openssl hashing functions expect as input.
Now that we have hashed the public key, we now perform base58check encoding. Base58check allows the hash to be displayed in a more compact way (using more letters of the alphabet) while avoiding characters that could be confused with each other such as 0 and O where a typo could result in your losing your funds. A checksum is applied to make sure the address was transmitted correctly without any data corruption such as mistyping the address.
Bitcoin P2PKH addresses begin with the version byte value 0x00 denoting the address type and end with a 4 byte checksum. First we prepend the version byte (prefix) to our public key hash and calculate and append the checksum before we encode it using base58 :
Note: -c denotes a checksum is to be applied. The checksum is calculated as checksum = SHA256(SHA256(prefix+data)) and only the first 4 bytes of the hash are appended to the end of the data.
The resulting value is a P2PKH address that can be used to receive Bitcoin: 16JrGhLx5bcBSA34kew9V6Mufa4aXhFe9X
Pay-to-Script Hash
The new default address type is a pay-to-script-hash, where instead of paying to a pubKey hash, it is a script hash. Bitcoin has a scripting language, you can read more about it here. Basically it allows for things like multiple signature requirements to send Bitcoin or a time delay before you are allowed to send funds, etc. A commonly used script is a P2WPKH (Pay to Witness Public Key Hash): OP_0 0x14
where the PubKey Hash is the RIPEMD160 of the SHA256 of the public key, as before, and 0x14 is the number of bytes in the PubKey Hash. So, to turn this script into an address, you simply apply BASE58CHECK to the RIPEMD160 of the SHA256 of the script OP_0 0x14
except you prepend 0x05 to the script hash instead of 0x00 to denote the address type is a P2SH address.
If you like the article, check out my course on how to Become a Bitcoin + Blockchain Programmer.
Источник
Bitcoin address
Enjoyed the article? Share:
Bitcoin address is an identifier (account number), starting with 1 or 3 and containing 27-34 alphanumeric Latin characters (except 0, O, I). Bitcoin addresses can be also represented as a QR-code. The addresses are anonymous and do not contain information about the owner. A bitcoin address can be obtained for free, using, for example, Bitcoin software. Bitcoin address example:
Addresses can be generated at no cost by any user of Bitcoin. For example, using Bitcoin Core, one can click «New Address» and be assigned an address. It is also possible to get a Bitcoin address using an account at an exchange or online wallet service.
There are currently two bitcoin address format in common use:
Common Pay-to-Pubkey Hash (P2PKH) which begin with the number 1. Newer Pay-to-Script Hash (P2SH) type starting with the number 3, eg: 35bSzXvRKLpHsHMrzb82f617cV4Srnt7hS .
Contents
What’s in a Bitcoin address [ edit ]
Most Bitcoin addresses are 34 characters. They consist of random digits and uppercase and lowercase letters, with the exception that the uppercase letter «O», uppercase letter «I», lowercase letter «l», and the number «0» are never used to prevent visual ambiguity.
Some Bitcoin addresses can be shorter than 34 characters (as few as 26) and still be valid. A significant percentage of Bitcoin addresses are only 33 characters, and some bitcoin address length may be even shorter.
Every Bitcoin address stands for a number. These shorter addresses are valid simply because they stand for numbers that happen to start with zeroes, and when the zeroes are omitted, the encoded address gets shorter.
Several of the characters inside a Bitcoin address are used as a checksum so that typographical errors can be automatically found and rejected. The checksum also allows Bitcoin software to confirm that a 33-character (or shorter) address is in fact valid and isn’t simply an address with a missing character.
Purpose and opportunities [ edit ]
Transfer/receive transactions of Bitcoins (Cryptocurrency, BTC) can be performed via address like the work with e-mail messages. One person can create an unlimited number of addresses, increasing the anonymity level of the payments. When performing the next transaction with BTC a new address is often created (the funds are credited/debited within 1-2 hours). At the same time the private key pair is generated, providing access to the identifier and the ability to perform transactions with currency. They are stored in the wallet.dat file on the user’s computer.
Input conditions [ edit ]
In order to avoid errors when manually inputting the address, it is recommended to use the clipboard. Symbols register is considered when you manually input the address. In case of incorrect input Bitcoins are sent to the wrong address or the transaction is rejected. Last one is done automatically if the identifier contains symbols that are used as a checksum (for verification).
The probability that a mistyped address is accepted as being valid is, approximately 1 in 4.29 billion.
How to create Bitcoin address? [ edit ]
The address is created by generating of random numbers and performing specific mathematical operations. It does not require Internet connection and registration at Bitcoin, where it begins to be monitored. Thousands of addresses (including personalized) and keys thereto can be generated within 1 minute, for example, when using Vanitygen utility.
Creating bitcoin address can be done without an Internet connection and does not require any contact or registration with the Bitcoin network. It is possible to create large batches of addresses offline using freely available software tools. Generating batches of addresses is useful in several scenarios, such as e-commerce websites where a unique pre-generated address is dispensed to each customer who chooses a «pay with Bitcoin» option. Newer «HD wallets» can generate a «seed» token which can be used to allow untrusted systems (such as webservers) to generate an unlimited number of addresses without the ability to spend the bitcoins received.
Transactions [ edit ]
Record of the BTC transfer from one address to another generates a transaction. It contains the hash of the previous transaction signed by the sender and Bitcoins recipients address. All information is sent to the Bitcoin network and after signatures verification transaction is accepted for processing.
Most Bitcoin wallets have a function to «sign» a message, proving the entity receiving funds with an address has agreed to the message. This can be used to, for example, finalise a contract in a cryptographically provable way prior to making payment for it.
Some services will also piggy-back on this capability by dedicating a specific address for authentication only, in which case the address should never be used for actual Bitcoin transactions. When you login to or use their service, you will provide a signature proving you are the same person with the pre-negotiated address.
It is important to note that these signatures only prove one receives with an address. Since Bitcoin transactions do not have a «from» address, you cannot prove you are the sender of funds.
Current standards for message signatures are only compatible with «version zero» bitcoin addresses (that begin with the number 1).
Bitcoin Address Validation [ edit ]
If you would like to validate a Bitcoin address in an application, it is advisable to use a method rather than to just check for string length, allowed characters, or that the address starts with a 1 or 3. Validation may also be done using open source code available in various languages or with an online validating tool.
Loss of Bitcoins [ edit ]
Loss of Bitcoins is possible in the following situations:
- if the wallet is lost because of the hard drive failure,
- when generating a new address, getting BTC on it and restoring the wallet from an earlier backup, where address is not yet created,
- when sending Bitcoins to address that doesn’t have owner.
Multi-signature Bitcoin address [ edit ]
Addresses can be created that require a combination of multiple private keys. Since these take advantage of newer features, they begin with the newer prefix of 3 instead of the older 1. These can be thought of as the equivalent of writing a check to two parties — «pay to the order of somebody AND somebody else» — where both parties must endorse the check in order to receive the funds.
The actual requirement (number of private keys needed, their corresponding public keys, etc.) that must be satisfied to spend the funds is decided in advance by the person generating this type of address, and once an address is created, the requirement cannot be changed without generating a new address.
Address balances [ edit ]
Addresses are not wallets nor accounts, and do not carry balances. They only receive funds, and you do not send «from» an address at any time. Various confusing services and software display bitcoins received with an address, minus bitcoins sent in random unrelated transactions as an «address balance», but this number is not meaningful: it does not imply the recipient of the bitcoins sent to the address has spent them, nor that they still have the bitcoins received.
An example of bitcoin loss resulting from this misunderstanding is when people believed their address contained 3 BTC. They spent 0.5 Bitcoins and believed the address now contained 2.5 BTC when actually it contained zero. The remaining 2.5 Bitcoins was transferred to a change address which was not backed up and therefore lost. This has happened on a few occasions to users of Paper wallets.
«From» addresses [ edit ]
Bitcoin transactions do not have any kind of origin-, source- or «from» address.
Источник